Chapter 21 Computational Geometry
http://www.csie.ntnu.edu.tw/~u91029/Point2.html
Relevent chapters: Matrix
Book: Computational Geometry Algorithms and Applications (Third Edition)
21.1 Rectangles Intersection
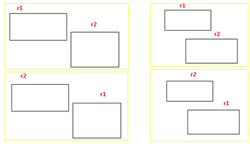
Write a function which will return TRUE when 2 rectangles are intersecting. Rectangles are passed as const RECT& r1, const RECT& r2. where RECT is a struct {int top, left, bottom, right;}
http://articles.leetcode.com/determine-if-two-rectangles-overlap/
21.2 223. Rectangle Area
Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane.
Each rectangle is defined by its bottom left corner and top right corner as shown in the figure.
Assume that the total area is never beyond the maximum possible value of int.
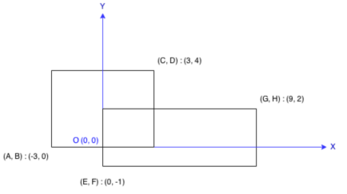
https://leetcode.com/problems/rectangle-area
http://www.cnblogs.com/scau20110726/archive/2013/04/12/3016765.html
http://www.voidcn.com/blog/roamer_nuptgczx/article/p-5930613.html
struct Solution {
int computeArea(int A, int B, int C, int D, int E, int F, int G, int H) {
int area1=(C-A)*(D-B), area2=(G-E)*(H-F);
if (C<=E || B>=H || A>=G || D<=F) return area1+area2;
vector <int> h={A,C,E,G};
vector <int> v={B,D,F,H};
sort(h.begin(), h.end());
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
return area1+area2 - (h[2] - h [1]) * (v[2] - v[1]);
}
};21.3 391. Perfect Rectangle
 https://leetcode.com/problems/perfect-rectangle/
https://leetcode.com/problems/perfect-rectangle/
- method 1:
http://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/52354018
C++:
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles){ //O(NLogN)
int area = 0;
set<pair<int, int>> sp;
for (auto& v : rectangles) { // O(N)
area += (v[2] - v[0])*(v[3] - v[1]);
if (sp.count({v[0],v[1]})) sp.erase({v[0],v[1]}); else sp.insert({v[0],v[1]});
if (sp.count({v[0],v[3]})) sp.erase({v[0],v[3]}); else sp.insert({v[0],v[3]});
if (sp.count({v[2],v[1]})) sp.erase({v[2],v[1]}); else sp.insert({v[2],v[1]});
if (sp.count({v[2],v[3]})) sp.erase({v[2],v[3]}); else sp.insert({v[2],v[3]});
}
return 4==sp.size()&&(sp.rbegin()->second-sp.begin()->second)*(sp.rbegin()->first-sp.begin()->first)==area;;
}- method 2:

http://blog.csdn.net/qq508618087/article/details/52483625
struct Solution { //O(N) Your runtime beats 47.92% of cpp submissions. 309ms.
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles){
unordered_map<string, int> hash;
for(auto val: rectangles){
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
string tem = to_string(val[i/2*2])+','+to_string(val[i%2*2+1]);
if(hash[tem]&(1<<i))
return false;
hash[tem] |= (1<<i);
}
}
int cntCorner = 0;
for(auto& val: hash){
int sec = val.second;
if(!(sec&(sec-1)) && cntCorner++ > 4) return false;
if((sec&(sec-1)) && !(sec==3||sec==12||sec==5||sec==10||sec==15))
return false;
}
return true;
}
};struct Solution {//Your runtime beats 94.86% of cpp submissions. 179ms.
#define F(x,y) tmp = ((long long)(v[x]) << 32) | v[y]; \
if (sp.count(tmp)) sp.erase(tmp); else sp.insert(tmp)
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
int minx = INT_MAX, miny = INT_MAX, maxy=INT_MIN, maxx=INT_MIN;
long long area=0;
for (auto& v : rectangles){
minx = min(v[0], minx), miny = min(v[1], miny),
maxx=max(maxx, v[2]), maxy=max(maxy, v[3]);
area += (v[2] - v[0])*(v[3] - v[1]);
}
if(area!=(maxx-minx)*(maxy-miny)) return false;
if (minx<0)for (auto& v : rectangles){ v[0] -= minx, v[2] -= minx;}
if (miny<0)for (auto& v : rectangles){ v[1] -= miny, v[3] -= miny;}
unordered_set<long long> sp;
long long mi=(((long long)(minx<0?0:minx)<<32)|(miny<0?0:miny));
long long mx=(((long long)(minx<0?maxx-minx:maxx)<<32)|(miny<0?maxy-miny:maxy)), tmp;
for (auto& v : rectangles) {F(0,1); F(0,3); F(2,1); F(2,3);}
return 4 == sp.size() && sp.count(mi) && sp.count(mx);
}
};struct pair_hash {
inline size_t operator()(const pair<int,int> & v) const{return v.first*31+v.second;}
};
struct Solution {//Your runtime beats 95.97% of cpp submissions. 172ms.
#define F(x,y) if (sp.count({v[x],v[y]})) sp.erase({v[x],v[y]}); else sp.insert({v[x],v[y]});
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
int minx = INT_MAX, miny = INT_MAX, maxy=INT_MIN, maxx=INT_MIN;
long long area=0;
unordered_set<pair<int, int>, pair_hash> sp;
for (auto& v : rectangles) {
F(0,1); F(0,3); F(2,1); F(2,3);
if(sp.size()<4) return false;
minx = min(v[0], minx), miny = min(v[1], miny), maxx=max(maxx, v[2]), maxy=max(maxy, v[3]);
area += (v[2] - v[0])*(v[3] - v[1]);
}
return 4 == sp.size() && sp.count({minx,miny}) && sp.count({maxx,maxy})
&&area==(maxx-minx)*(maxy-miny);
}
};21.4 356. Line Reflection
Given n points on a 2D plane, find if there is such a line parallel to y-axis that reflect the given set of points.
Example 1: Given points = [[1,1],[-1,1]], return true. Example 2: Given points = [[1,1],[-1,-1]], return false.
Follow up: Could you do better than \(O(N^2)\)?
Hint: Find the smallest and largest x-value for all points. If there is a line then it should be at y = (minX + maxX) / 2. For each point, make sure that it has a reflected point in the opposite side.
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/5579271.html
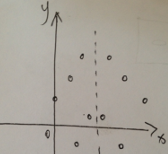
我们采取的做法是:把坐标都放到一个set中,如果所有的点都是关于某个与y轴平行的轴对称的话,那么他们的x坐标相加之和肯定是相同的,所以对于数组中的每一个点(p[0],p[1]),都要判断(sum-p[0],p[1])是否在set中,如果有一个不在,说明不满足,直接返回false;如果都在,说明满足条件,返回true.
如何判断两个矩形相交
http://blog.csdn.net/orbit/article/details/7368996
If a point inside a polygon? http://www.html-js.com/article/1517
已知两个多边形Poly1和Poly2,分别由点集C1={P1,P2,…,Pm}和C2={Q1,Q2,…,Qn}表示,求这两个多边形的交集 http://www.cnblogs.com/dwdxdy/p/3232110.html
21.5 469. Convex Polygon
Given a list of points that form a polygon when joined sequentially, find if this polygon is convex (Convex polygon definition).
http://leetcode.com/problems/convex-polygon/
http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2016/12/04/leetcode-convex-polygon/
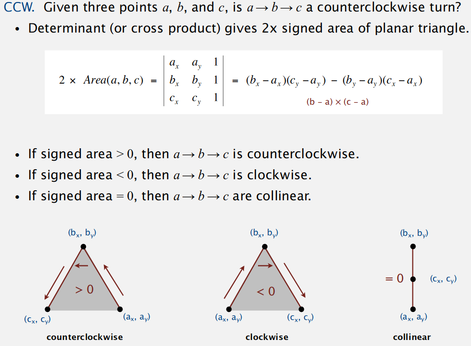
这道题是靠叉积的运用.CLRS33章第一节的内容.
- 向量叉积的公式
/*
计算向量的叉积(ABxAC A(x0,y0) B(x1,y1) C(x2,y2))是计算行列式
| x1-x0 y1-y0 |
| x2-x0 y2-y0 |
的结果(向量的叉积 AB X AC)
*/- Convex Hull
遍历顶点,判断相邻三个顶点A、B、C组成的两个向量(AB, AC)的叉积是否同负同正.
- Rolling array loop
int L = points.size();
for (int i=0; i<L; i++){
points[i], points[(i+1)%L], points[(i+2)%L];
}同样的模板在Game of Life也出现过.
struct Solution { // 69ms
int dot_product(vector<int>& p0, vector<int>& p1, vector<int>& p2){
return (p1[0]-p0[0])*(p2[1]-p0[1]) - (p2[0]-p0[0])*(p1[1]-p0[1]);
}
bool isConvex(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int L=points.size();
long long last=0;
for(int i=0; i<L; ++i){
vector<int>& p0 = points[i];
vector<int>& p1 = points[(i+1)%L];
vector<int>& p2 = points[(i+2)%L];
int t = dot_product(p0,p1,p2);
if (t*last < 0) return false; // 1. overflow
if(t) last=t; // 2. ignore 0
}
return true;
}
};
struct Solution { // AC
bool isConvex(vector<vector<int>>& p) {
long n = p.size(), prev = 0, cur;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
vector<vector<int>> A; // = {p[(i+1)%n]-p[i], p[(i+2)%n]-p[i]}
for (int j = 1; j < 3; ++j) A.push_back({p[(i+j)%n][0]-p[i][0], p[(i+j)%n][1]-p[i][1]});
if (cur = det2(A)) if (cur*prev < 0) return false; else prev = cur;
}
return true;
}
// calculate determinant of 2*2 matrix A
long det2(vector<vector<int>>& A) { return A[0][0]*A[1][1] - A[0][1]*A[1][0]; }
};值得注意的两点是:
1. int overflow, 所以last用long long.
2. 如果本次计算结果为0,不会影响判断.
21.6 Convex Hull with Graham’s Scan
CCW - Positive Area
http://www.cnblogs.com/devymex/archive/2010/08/09/1795392.html
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
//二维点(或向量)结构体定义
struct POINT { int x; int y; };
typedef vector<POINT> PTARRAY;
//判断两个点(或向量)是否相等
bool operator==(const POINT &pt1, const POINT &pt2) {
return (pt1.x == pt2.x && pt1.y == pt2.y);
}
// 比较两个向量pt1和pt2分别与x轴向量(1, 0)的夹角
bool CompareVector(const POINT &pt1, const POINT &pt2) {
//求向量的模
float m1 = sqrt((float)(pt1.x * pt1.x + pt1.y * pt1.y));
float m2 = sqrt((float)(pt2.x * pt2.x + pt2.y * pt2.y));
//两个向量分别与(1, 0)求内积
float v1 = pt1.x / m1, v2 = pt2.x / m2;
return (v1 > v2 || (v1 == v2 && m1 < m2));
}
//计算凸包
void CalcConvexHull(PTARRAY &vecSrc) {
//点集中至少应有3个点,才能构成多边形
if (vecSrc.size() < 3) {
return;
}
//查找基点
POINT ptBase = vecSrc.front(); //将第1个点预设为最小点
for (PTARRAY::iterator i = vecSrc.begin() + 1; i != vecSrc.end(); ++i) {
//如果当前点的y值小于最小点,或y值相等,x值较小
if (i->y < ptBase.y || (i->y == ptBase.y && i->x > ptBase.x)) {
//将当前点作为最小点
ptBase = *i;
}
}
//计算出各点与基点构成的向量
for (PTARRAY::iterator i = vecSrc.begin(); i != vecSrc.end();) {
//排除与基点相同的点,避免后面的排序计算中出现除0错误
if (*i == ptBase) {
i = vecSrc.erase(i);
}
else {
//方向由基点到目标点
i->x -= ptBase.x, i->y -= ptBase.y;
++i;
}
}
//按各向量与横坐标之间的夹角排序
sort(vecSrc.begin(), vecSrc.end(), &CompareVector);
//删除相同的向量
vecSrc.erase(unique(vecSrc.begin(), vecSrc.end()), vecSrc.end());
//计算得到首尾依次相联的向量
for (PTARRAY::reverse_iterator ri = vecSrc.rbegin();
ri != vecSrc.rend() - 1; ++ri) {
PTARRAY::reverse_iterator riNext = ri + 1;
//向量三角形计算公式
ri->x -= riNext->x, ri->y -= riNext->y;
}
//依次删除不在凸包上的向量
for (PTARRAY::iterator i = vecSrc.begin() + 1; i != vecSrc.end(); ++i) {
//回溯删除旋转方向相反的向量,使用外积判断旋转方向
for (PTARRAY::iterator iLast = i - 1; iLast != vecSrc.begin();) {
int v1 = i->x * iLast->y, v2 = i->y * iLast->x;
//如果叉积小于0,则无没有逆向旋转
//如果叉积等于0,还需判断方向是否相逆
if (v1 < v2 || (v1 == v2 && i->x * iLast->x > 0 &&
i->y * iLast->y > 0)) {
break;
}
//删除前一个向量后,需更新当前向量,与前面的向量首尾相连
//向量三角形计算公式
i->x += iLast->x, i->y += iLast->y;
iLast = (i = vecSrc.erase(iLast)) - 1;
}
}
//将所有首尾相连的向量依次累加,换算成坐标
vecSrc.front().x += ptBase.x, vecSrc.front().y += ptBase.y;
for (PTARRAY::iterator i = vecSrc.begin() + 1; i != vecSrc.end(); ++i) {
i->x += (i - 1)->x, i->y += (i - 1)->y;
}
//添加基点,全部的凸包计算完成
vecSrc.push_back(ptBase);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int nPtCnt = 100; //生成的随机点数
PTARRAY vecSrc, vecCH;
for (int i = 0; i < nPtCnt; ++i) {
POINT ptIn = { rand() % 20, rand() % 20 };
vecSrc.push_back(ptIn);
cout << ptIn.x << ", " << ptIn.y << endl;
}
CalcConvexHull(vecSrc);
cout << "\nConvex Hull:\n";
for (PTARRAY::iterator i = vecSrc.begin(); i != vecSrc.end(); ++i) {
cout << i->x << ", " << i->y << endl;
}
return 0;
}21.7 587. Erect the Fence
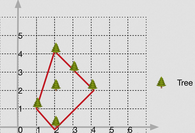
There are some trees, where each tree is represented by (x,y) coordinate in a two-dimensional garden. Your job is to fence the entire garden using the minimum length of rope as it is expensive. The garden is well fenced only if all the trees are enclosed. Your task is to help find the coordinates of trees which are exactly located on the fence perimeter.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]]
Explanation:
https://leetcode.com/problems/erect-the-fence
21.7.1 Algo 1: Monotone Chain
http://www.cnblogs.com/weedboy/p/6896478.html
http://bit.ly/2vQOBd5
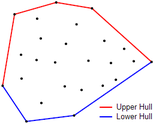
class Solution {
long long cross(const Point &O,const Point &A,const Point &B){
return (A.x-O.x)*(long long)(B.y-O.y) - (A.y-O.y)*(long long)(B.x-O.x);
}
public:
vector<Point> outerTrees(vector<Point>& points) {
int L=points.size(), k=0;
vector<Point> r(2*L);
auto cmp=[](Point& p1, Point& p2){
return p1.x<p2.x ||(p1.x==p2.x && p1.y<p2.y);};
auto equ=[](Point& p1, Point& p2){
return (p1.x==p2.x && p1.y==p2.y);};
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), cmp);
for(int i=0;i<L;++i){ // lower hull
while(k>=2 && cross(r[k-2],r[k-1],points[i])<0) k--;
r[k++]=points[i];
}
for(int i=L-2,t=k+1;i>=0;i--){ // upper hull
while(k>=t && cross(r[k-2],r[k-1],points[i])<0) k--;
r[k++]=points[i];
}
r.resize(k), sort(r.begin(), r.end(), cmp);
r.erase(unique(r.begin(), r.end(), equ), r.end());
return r;
}
};21.8 Closest Pair of Points
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/closest-pair-of-points/
http://blog.csdn.net/u013522065/article/details/44810915