Chapter 11 Skip List
SkipList在leveldb,Redis以及lucence中都广为使用,是比较高效的数据结构.
Skip lists are data structures that use probabilistic balancing rather than strictly enforced balancing. As a result, the algorithms for insertion and deletion in skip lists are much simpler and significantly faster than equivalent algorithms for balanced trees.
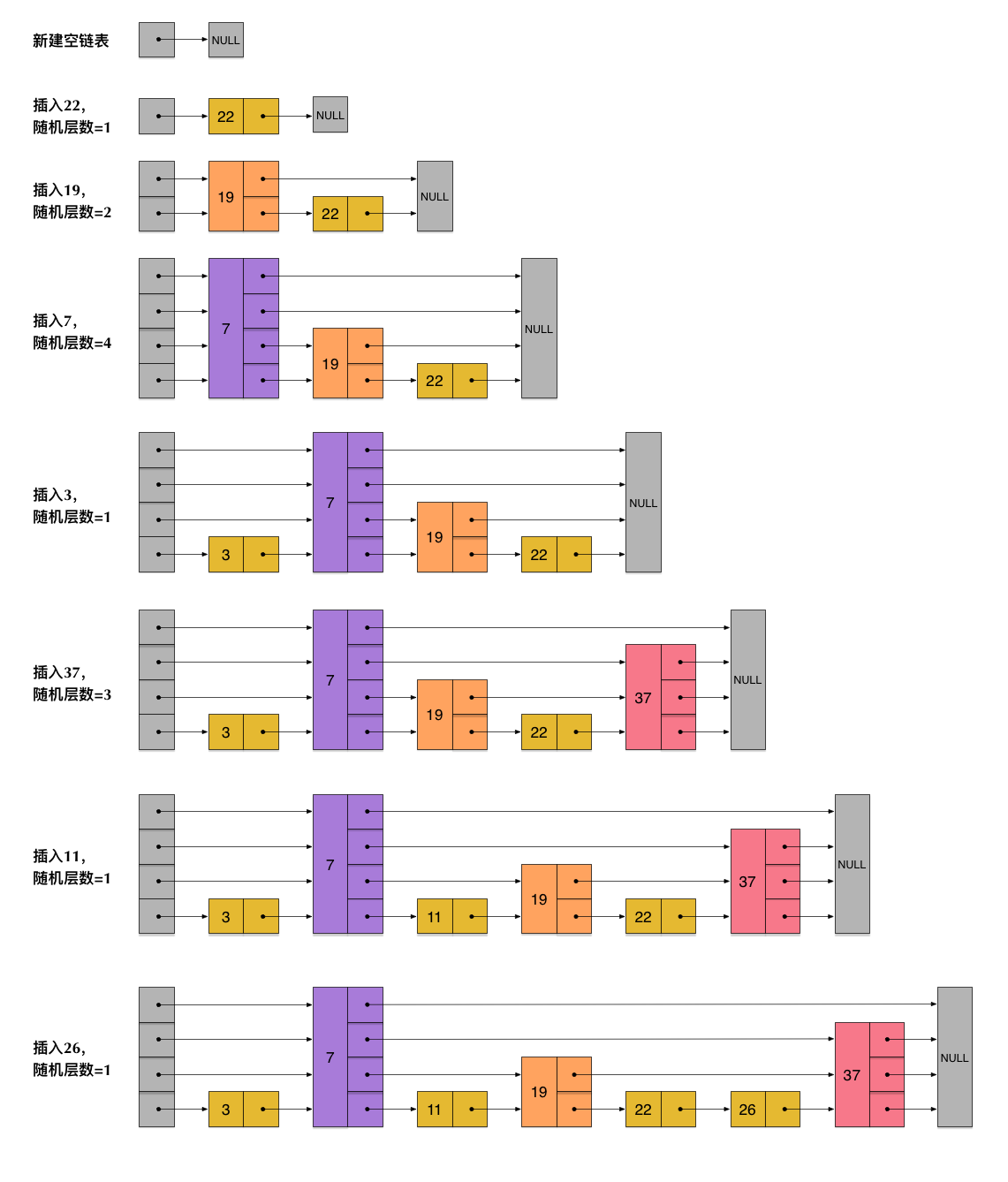
From: http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
http://www.drdobbs.com/cpp/skip-lists-in-c/184403579 对随机函数的解释不错.
http://www.cnblogs.com/wuchanming/p/3870355.html
http://www.cppblog.com/mysileng/archive/2013/04/06/199159.html
- Facebook’s thread safe skiplist implementation:
https://github.com/facebook/folly/blob/master/folly/ConcurrentSkipList.h
Redisskiplist implementation in file t_zset.c
35 /* ZSETs are ordered sets using two data structures to hold the same elements
36 * in order to get O(log(N)) INSERT and REMOVE operations into a sorted
37 * data structure.
38 *
39 * The elements are added to a hash table mapping Redis objects to scores.
40 * At the same time the elements are added to a skip list mapping scores
41 * to Redis objects (so objects are sorted by scores in this "view").
42 *
43 * Note that the SDS string representing the element is the same in both
44 * the hash table and skiplist in order to save memory. What we do in order
45 * to manage the shared SDS string more easily is to free the SDS string
46 * only in zslFreeNode(). The dictionary has no value free method set.
47 * So we should always remove an element from the dictionary, and later from
48 * the skiplist.
49 *
50 * This skiplist implementation is almost a C translation of the original
51 * algorithm described by William Pugh in "Skip Lists: A Probabilistic
52 * Alternative to Balanced Trees", modified in three ways:
53 * a) this implementation allows for repeated scores.
54 * b) the comparison is not just by key (our 'score') but by satellite data.
55 * c) there is a back pointer, so it's a doubly linked list with the back
56 * pointers being only at "level 1". This allows to traverse the list
57 * from tail to head, useful for ZREVRANGE. */http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
随机函数的设计:
Assume the MaxHeight of a node is 4, 那么总共有5个高度[0,1,2,3,4]. I want \(P(H=1)/P(H=0) = 0.5\), \(P(H=2)/P(H=1) = 0.5\), 而且逐层以此类推. 这个随机函数可以这样设计:
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
using namespace std;
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 32
#define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25
srandom(time(0));
int zslRandomLevel(void) { //35022411
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
vector<int> v(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0);
struct timeval tv; gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
unsigned long t1 = 1000000 * tv.tv_sec + tv.tv_usec;
for(int i=(0x7fffffff>>2);i>=0;i--) v[zslRandomLevel()-1]++;
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
cout << 1000000 * tv.tv_sec + tv.tv_usec - t1 << endl;
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout,","));
/*> heights=c(268447157,134211631,67112895,33548149,16771904,
8390171,4193819,2099876,1047421,524590,262148,
130599,65040,32602,16516,8119,4117,2074,1029,
508,265,157,65,28,20,4,4,2,1,1,0,0)
> plot(heights,type='o')*/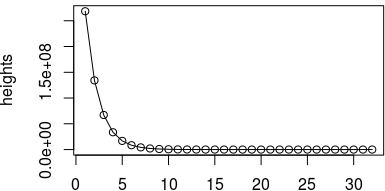
我不明白为什么redis的skiplist的随机高度函数写成那样.难道是某些系统没有定义RAND_MAX?
我下面的两种方法经过测试都比上面的速度快,结果也正确.
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1, t = ZSKIPLIST_P*RAND_MAX;
while (random()<t) ++level;
return min(level,ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL);
}当ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL较小的时候,或者ZSKIPLIST_P比较大的时候,这个更快:
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1, t = ZSKIPLIST_P*RAND_MAX;
while (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL && random()<t) ++level;
return level;
}这个给levelDB的方法比较接近,但是那个是用的modulo,所以我觉得速度会慢些.
Redis中的SkipList相当于是一棵四叉树.(1/ZSKIPLIST_P)是树的叉数.
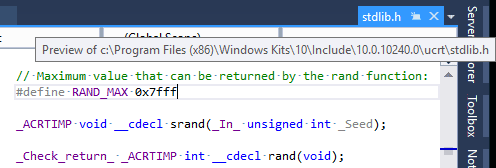
RAND_MAX: Maximum value returned byrand()orrandom(). This macro expands to an integral constant expression whose value is the maximum value returned by the rand function. This value islibrary-dependent, but is guaranteed to be at least32767on any standard library implementation.
- Microsoft C Standard Library
<stdlib.h>header:
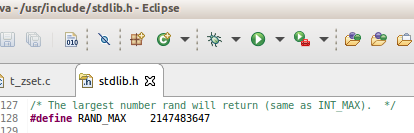
- GNU C Library:
http://www.cnblogs.com/liuhao/archive/2012/07/26/2610218.html
http://yaronspace.cn/blog/archives/1259
- skiplist in
leveldb
http://luodw.cc/2015/10/16/leveldb-05/
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key,Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = 4;
int height = 1;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == 0)) {
height++;
}
assert(height > 0);
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
}和redis里面的一样,也是一个四叉树.
- skiplist in
lucene
http://www.cnblogs.com/forfuture1978/archive/2009/12/14/1623597.html
http://www.dongcoder.com/detail-309748.html
- lock free skiplist
http://ifeve.com/cas-skiplist/
- 用skip list实现实时排名?
http://wangyuanzju.blog.163.com/blog/static/1302920099311165490/
浅析SkipList跳跃表原理及代码实现
http://blog.csdn.net/ict2014/article/details/17394259
- ebay interview
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/53673/search-an-element-in-the-skip-list
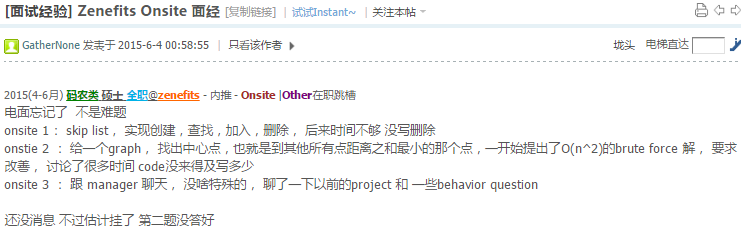
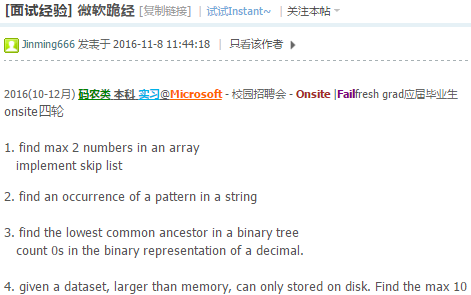
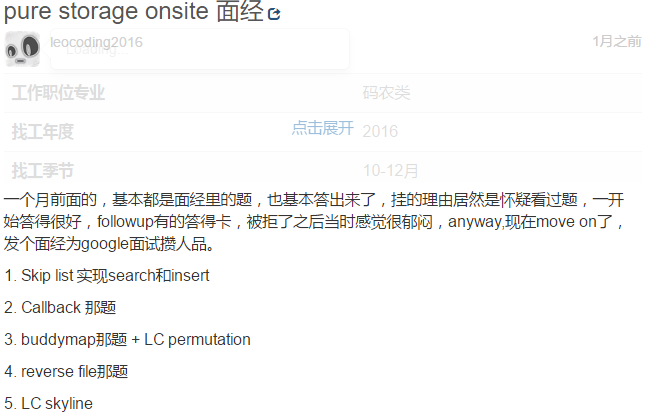
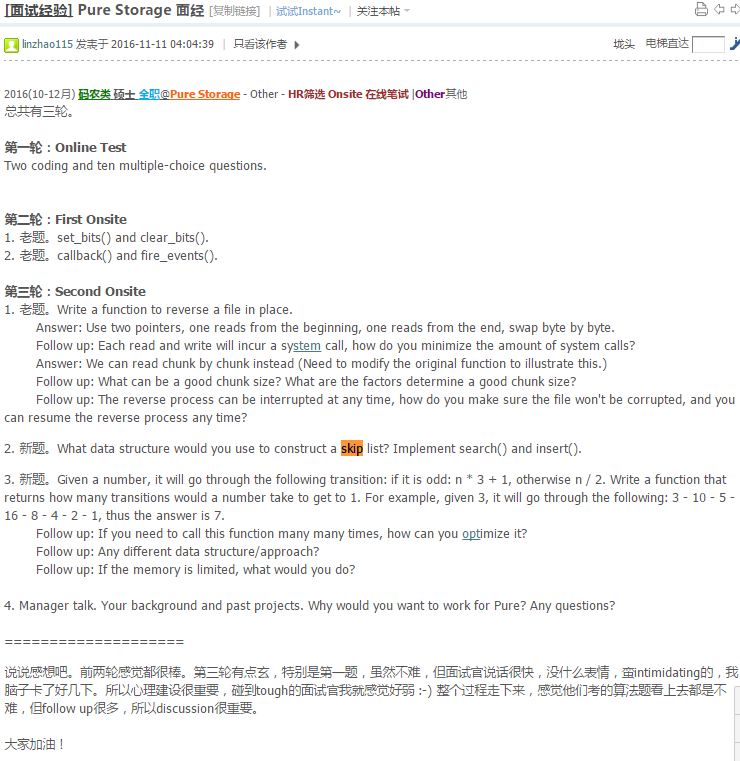
- My implementation:
#pragma once
#include "henry.h"
#include <random>
namespace _skiplist {
#define MAXLEVEL 5
#define THRESHOLD 0.5*RAND_MAX
struct SkipListNode {
int key, value, level; //
SkipListNode* forward[MAXLEVEL]; //
};
struct SkipList {
SkipListNode* head;
int level; //
int length; //
};
SkipListNode* makeNode(int level, int key, int value) {
SkipListNode* pNode = new SkipListNode;
pNode->key = key;
pNode->value = value;
pNode->level = level;
for (int i = 0; i < MAXLEVEL; ++i)
pNode->forward[i] = NULL;
return pNode;
}
void initSkipList(SkipList *pSkipList) {
if (!pSkipList)
return;
SkipListNode* head = makeNode(0, 0, 0);
if (!head)
return;
pSkipList->head = head;
pSkipList->length = 0;
pSkipList->level = 1;
for (int i=0; i < MAXLEVEL; i++)
pSkipList->head->forward[i] = NULL;
}
int randomLevel(){ // [1,MAXLEVEL]
for(int r=1;r<MAXLEVEL && rand()<THRESHOLD; ++r);
return r;
}
bool insertNode(SkipList *pSkipList, int searchKey, int newValue){
SkipListNode* update[MAXLEVEL];
if (!pSkipList)
return false;
SkipListNode* cur = pSkipList->head;
for (int i = pSkipList->level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (cur->forward[i] && cur->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
cur = cur->forward[i];
update[i] = cur;
}
cur = cur->forward[0];
if (cur && cur->key == searchKey) {
cur->value = newValue;
} else {
int k = randomLevel();
if (k > pSkipList->level) {
for (int i = pSkipList->level; i < k; i++)
update[i] = pSkipList->head;
pSkipList->level = k;
}
cur = makeNode(k, searchKey, newValue);
for (int i = 0; i < pSkipList->level; ++i) {
cur->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = cur;
}
pSkipList->length++;
}
return true;
}
SkipListNode* searchNode(SkipList *pSkipList, int searchKey) {
if (!pSkipList)
return NULL;
SkipListNode *pNode = pSkipList->head;
if (!pNode)
return NULL;
for (int i = pSkipList->level - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
while (pNode->forward[i] && pNode->forward[i]->key < searchKey)
pNode = pNode->forward[i];
}
pNode = pNode->forward[0];
if (pNode && pNode->key == searchKey)
return pNode;
return NULL;
}
bool deleteNode(SkipList* pSkipList, int searchKey) {
if (!pSkipList)
return false;
SkipListNode *pNode = pSkipList->head;
SkipListNode *update[MAXLEVEL];
for (int i = pSkipList->level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (pNode->forward[i] && pNode->forward[i]->key < searchKey) {
pNode = pNode->forward[i];
}
update[i] = pNode;
}
pNode = pNode->forward[0];
if (pNode && pNode->key == searchKey) {
for (int i = 0; i < pSkipList->level; ++i) {
if (update[i] && update[i]->forward[i] != pNode) {
break;
}
update[i]->forward[i] = pNode->forward[i];
}
free(pNode);
while (pSkipList->level > 1 &&
pSkipList->head->forward[pSkipList->level - 1] == NULL) {
pSkipList->level--;
}
pSkipList->length--;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void travelList(SkipList* pSkipList) {
SkipListNode* pNode = pSkipList->head;
if (!pNode)
return;
while (pNode->forward[0]) {
cout << pNode->forward[0]->value << " " << pNode->forward[0]->level << endl;
pNode = pNode->forward[0];
}
}
int test() {
SkipList list;
initSkipList(&list);
insertNode(&list, 10, 10);
insertNode(&list, 2, 2);
insertNode(&list, 5, 5);
travelList(&list);
SkipListNode* pNode = searchNode(&list, 2);
cout << pNode->value << endl;
pNode = searchNode(&list, 10);
cout << pNode->value << endl;
cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, 2);
travelList(&list);
cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, 10);
travelList(&list);
cout << "----" << endl;
deleteNode(&list, 7);
travelList(&list);
return 0;
}
}