Chapter 52 Linkedin 2016 11
52.1 384. Shuffle an Array
Shuffle a set of numbers without duplicates.
Example:
// Init an array with set 1, 2, and 3.
int[] nums = {1,2,3};
Solution solution = new Solution(nums);
// Shuffle the array [1,2,3] and return its result.
// Any permutation of [1,2,3] must equally likely to be returned.
solution.shuffle();
// Resets the array back to its original configuration [1,2,3].
solution.reset();
// Returns the random shuffling of array [1,2,3].
solution.shuffle(); https://leetcode.com/problems/shuffle-an-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shuffle-an-array/
因为这题要求保留原始数组,所以S必须是O(N),因此naive和渔夫都可以用.
class Solution {
vector<int> v;
public:
Solution(vector<int> nums) {
v=nums;
}
/** Resets the array to its original configuration and return it. */
vector<int> reset() {
return v;
}
/** Returns a random shuffling of the array. */
vector<int> shuffle() {
vector<int> t=v;
for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++)
swap(t[i],t[i+rand()%(t.size()-i)]);
return t;
}
};
渔夫洗牌算法Fisher–Yates shuffle Algorithm works in O(n) time complexity. The assumption here is, we are given a function rand() that generates random number in \(O(1)\) time.
渔夫洗牌的两种形式,wikipedia说得很详细:
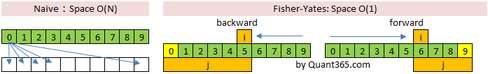
-- To shuffle an array a of n elements (indices 0..n-1):
for i from n−1 downto 1 do
j ← random integer such that 0 ≤ j ≤ i
exchange a[j] and a[i]C++实现1:
void shuffle1(vector<int>& vi){
int L=vi.size();
for(int i=L-1; i>=1; i--)
swap(vi[rand() % (i+1)],vi[i]); //注意是i+1
}-- To shuffle an array a of n elements (indices 0..n-1):
for i from 0 to n−2 do
j ← random integer such that i ≤ j < n
exchange a[i] and a[j]C++实现2:
void shuffle2(vector<int>& vi){
int L=vi.size();
for(int i=0; i<L-1; i++)
swap(vi[i + rand()%(L-i)],vi[i]); //注意这里繁琐点
}http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/shuffle-a-given-array/
一般采用第一种方法.
OJ: http://code.geeksforgeeks.org/09ulgx
概率证明(*)
- Naive Method
1->1: \(\frac{1}{n}\)
2->1: \(\frac{n-1}{n} \frac{1}{n-1} = \frac{1}{n}\)
…
Probability of ith element goes to jth cell is \(\frac{1}{n}\).
- 渔夫洗牌
The probability that ith element (including the last one) goes to last position is 1/n, because we randomly pick an element in first iteration.
The probability that ith element goes to second last position can be proved to be 1/n by dividing it in two cases.
Case 1: \(i = n-1\) (index of last element):
The probability of last element going to second last position is = (probability that last element doesn’t stay at its original position) x (probability that the index picked in previous step is picked again so that the last element is swapped) So the probability = \(\frac{n-1}{n} \frac{1}{n-1} = \frac{1}{n}\)
Case 2: \(0 < i < n-1\) (index of non-last):
The probability of ith element going to second last position = (probability that ith element is not picked in previous iteration) x (probability that ith element is picked in this iteration) So the probability = \(\frac{n-1}{n} \frac{1}{n-1} = \frac{1}{n}\)
We can easily generalize above proof for any other position. 所以ith element最后被放去任意格的概率都是\(1/n\).
52.2 235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 _4 7 9
/ \
3 5For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree
http://www.cnblogs.com/yrbbest/p/5003610.html
public class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || p == null || q == null)
return root;
if(p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
else if(p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val)
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
else
return root;
}
}52.3 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
 https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
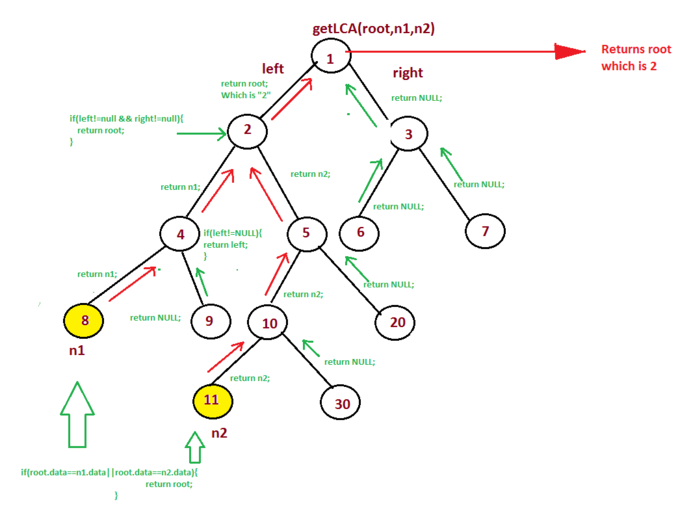
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
// 如果当前节点为空或者与目标节点之一相同,则返回当前节点
if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root;
// 递归寻找p和q在左右子树中的位置
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
//如果p和q分别位于root的左右两侧(subcall都返回non-empty),
//则root为它们的LCA,否则为左子树或者右子树
return !left ? right : !right ? left : root; //注意这种语法
}下面这种写法可能更好理解:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root or root==p or root==q) return root;
auto l = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
auto r = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(l && r) return root;
return l?l:r;
}- Follow up
52.4 254. Factor Combinations
http://leetcode.com/problems/factor-combinations/
input: 32
output:
[
[2, 16],
[2, 2, 8],
[2, 2, 2, 4],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[2, 4, 4],
[4, 8]
]http://segmentfault.com/a/1190000005801106
http://www.jianshu.com/p/9a883428cebb
不错的分析: http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/5332722.html
写出所有的因子相乘的形式,而且规定了因子从小到大的顺序排列.
- Algo 1 - cherry pick at leaf node
可以用DFS traverse in the following divisor tree. 因为factor(divisor) are listed in non-descending order, child node must be greater than parent node. 如下图所示,叶节点为绿色代表一条通路.我们会遇到一些无效的路径,比如图中2->8之后就走不下去了,因为下一个可能的节点是2,但是2比8小.
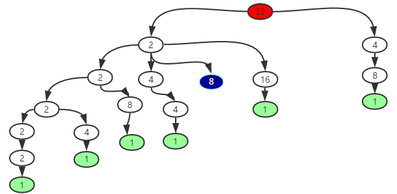
struct Solution { // 189ms
vector<vector<int>> getFactors(int n) { // 12
vector<vector<int>> r;
vector<int> p;
dfs(r, p, 2, n);
return r;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& r, vector<int>& p, int divisor, int dividend) {
if (dividend == 1) {if (p.size()>1) r.push_back(p); return;}
for (int i = divisor; i <= dividend; ++i) {
if (dividend%i == 0) { // i是被除数,n/i是相除的结果
p.push_back(i);
// why 3rd parameter is i, because 因子从小到大的顺序排列
dfs(r, p, i, dividend / i);
p.pop_back();
}
}
}
};DFS traverse until the leaf node is 1, then we do cherry pick.
- Algo 2 - cherry pick at every child node
 最优的解法是利用这个特殊的factor tree. Tree node has two parts:
最优的解法是利用这个特殊的factor tree. Tree node has two parts: divisorandquotient. We use quotient to find child node, divisor is the starting point of next level’s divisor:
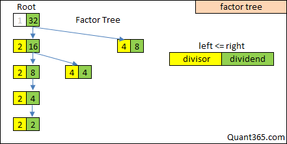
Loop i in [initial value of divisor,sqrt(dividend)] to find dividend%i==0, which is the next child.
和subset那道题一样,cherry pick
at every child node,而不是仅仅在leaf node.所以速度比上面的解法快几十倍.
struct Solution { // 3ms
vector<vector<int>> getFactors(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> r;
helper(r, {}, n, 2);
return r;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>> &r, vector<int> p,
int dividend, int divisor)
{
for (int i = divisor; i <= sqrt(dividend); ++i) {
if (dividend % i == 0) {
vector<int> t = p;
t.push_back(i);
helper(r, t, dividend / i, i);
t.push_back(dividend / i);
r.push_back(t);
}
}
}
};还要注意这里p不在是以前的partial solution,其实是累积的所有divisor. t其实才是partial solution,t最后加上了quotient然后cherry pick到r里面. 在stackframe之间传递的是cumuliative divisors,不是partial solution,或者说是一种特殊的partial solution. 这是不同于以往的case的地方.After all, there are two parts in one node in our factor tree.
- Algo 3
上面两种方法得到的结果跟题目中给的答案的顺序不同,虽然顺序不同,但是并不影响其通过OJ.我们下面就给出生成题目中的顺序的解法,这种方法也不难理解,还是从2遍历到n的平方根,如果i是因子,那么我们递归调用n/i,结果用v来保存,然后我们新建一个包含i和n/i两个因子的序列out,然后将其存入结果r, 然后我们再遍历之前递归n/i的所得到的序列,如果i小于等于某个序列的第一个数字,那么我们将其插入该序列的首位置,然后将序列存入结果r中,我们举个例子,比n = 12,那么刚开始i = 2,是因子,然后对6调用递归,得到{2, 3},然后此时将{2, 6}先存入结果中,然后发现i(此时为2)小于等于{2, 3}中的第一个数字2,那么将2插入首位置得到{2, 2, 3}加入结果,然后此时i变成3,还是因子,对4调用递归,得到{2, 2},此时先把{3, 4}存入结果,然后发现i(此时为3)大于{2, 2}中的第一个数字2,不做任何处理直接返回,这样我们就得到正确的结果了:
struct Solution { // 9-13ms
vector<vector<int>> getFactors(int n) {
vector<vector<int>> r;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; ++i) {
if (n % i == 0) {
vector<vector<int>> v = getFactors(n / i);
vector<int> out{ i, n / i };
r.push_back(out);
for (auto a : v) {
if (i <= a[0]) {
a.insert(a.begin(), i);// 慢,从头插入
r.push_back(a);
}
}
}
}
return r;
}
};复杂度: Loop次数, 递归次数, push to vector次数
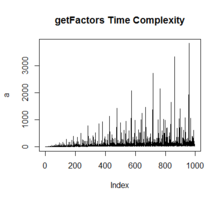
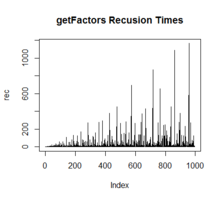
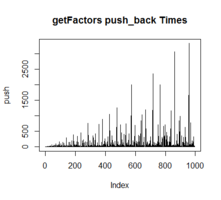
52.5 170. Two Sum III - Data structure design

 https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iii-data-structure-design/
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum-iii-data-structure-design/
Design and implement a TwoSum class. It should support the following operations: add and find.
add - Add the number to an internal data structure. find - Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value.
add(1); add(3); add(5);
find(4) -> true
find(7) -> false1. Add多find少
Two Sum的時候是用hashtable實時的查找.這道題也是用hashtable查找,但是不一樣的地方是hashtable預先建好的.
所以單純的hashtable是不夠的,比如這個Edge case: [1] 查找2應該是false
應該用一個counter,如果有這種edge case的情況,查看count是否大於1.
ONE COUNTER ( unordered_map )
struct TwoSum {
unordered_map<int, int> counter;
void add(int number) { counter[number]++; } //O(1)
bool find(int t) {
for(auto pr: counter){ // O(N)
int val = t - pr.first;
if ((val != pr.first && counter.count(val))||(t==pr.first && pr.second>1))
return true;
}
return false;
}
};2. Add少find多
TWO SETs - edge case是重复数字.
52.7 339. Nested List Weight Sum
 https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum/
https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum/
int depthSum(vector<NestedInteger>& nestedList) {
int r = 0;
for(auto e: nestedList) dfs(r, e, 1); // level 1 must be a list
return r;
}
void dfs(int& r, NestedInteger& ni, int level){
if(ni.isInteger())
r += ni.getInteger() * level;
else
for(NestedInteger& e : ni.getList()) dfs(r,e,level+1);
}- Nested List Weight Sum II
 https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/nested-list-weight-sum-ii/
参考: http://sde.quant365.com/free-treebinary-tree.html#nested-list-weight-sum-ii
52.8 Shortest Word Distance Series
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000003906667
- Shortest Word Distance
 https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance/
Given a list of words and two words word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two words in the list.
For example, Assume that words = [“practice”, “makes”, “perfect”, “coding”, “makes”].
Given word1 = “coding”, word2 = “practice”, return 3. Given word1 = “makes”, word2 = “coding”, return 1.
- Algo 1 - 数据结构:
index map
笨办法 T:\(O(N^2)\), S:\(O(N)\)
int shortestDistance(vector<string>& words, string word1, string word2) {
unordered_map<string, vector<int>> mv;
int i=0, r=INT_MAX;
for(auto s: words) mv[s].push_back(i++);
vector<int> s1 = mv[word1], s2=mv[word2];
for(int i: s1) for(int j: s2) r=min(r,abs(i-j));
return r;
}- Algo 2
其实不需要index map
 T:\(O(N)\), S:\(O(1)\):
T:\(O(N)\), S:\(O(1)\):
int shortestDistance(vector<string>& ws, string w1, string w2) {//19ms
int r=INT_MAX, idx1=-1, idx2=-1;
for(int i=0;i<ws.size();++i){
if(ws[i]==w1){
idx1=i;
if(idx2>=0) r= min(r,i-idx2);
}else if(ws[i]==w2){
idx2=i;
if(idx1>=0) r= min(r,i-idx1);
}
}
return r;
}- Shortest Word Distance II
 https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-ii/
数据结构: index map 算法: Two pointer
struct WordDistance { // 55ms
unordered_map<string, vector<int>> m;//
WordDistance(vector<string>& words) {
int i=0;
for(auto s: words) m[s].push_back(i++);
}
int shortest(string w1, string w2) { // O(N)
auto v1=m[w1], v2=m[w2];
int i=0, j=0, r=INT_MAX;
while(i<v1.size() && j<v2.size()){
r = min(r,abs(v1[i]-v2[j]));
if(v1[i]<v2[j]) i++; else j++;
}
return r;
}
};我感觉其实可以把结果cache起来.这样shortest可以做到\(O(1)\). 不过这样很耗空间.n个单词有\(n*(n-1)/2\)个pair.
- Shortest Word Distance III
 https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-iii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-word-distance-iii/
沿用II的思路:
int shortestWordDistance(vector<string>& words, string word1, string word2) {//55ms
unordered_map<string, vector<int>> m;
int i=0, j = 0, r=0x7fffffff;
for (string& w : words) m[w].push_back(i++); // N
vector<int>& v1 = m[word1];
vector<int>& v2 = m[word2];
if(word1==word2){
for(int k=0; k<v1.size()-1; ++k) // K
r=min(r, v1[k+1]-v1[k]);
return r;
}
i = 0;
while (i<v1.size() && j<v2.size()){ // K
r = min(r, abs(v1[i]-v2[j]));
if(v1[i]<v2[j]) i++;
else if(v1[i]>v2[j]) j++;
else return 0;
}
return r;
}沿用I的思路:
int shortestWordDistance(vector<string>& ws, string w1, string w2) {//16ms
int r=INT_MAX;
if(w1==w2){
for(int i=0, j=-1;i<ws.size();++i)
if(ws[i]==w1) {
if(j>=0) r=min(r, i-j);
j=i;
}
return r;
}
for(int i=0,idx1=-1,idx2=-1;i<ws.size();++i){
if(ws[i]==w1){
idx1=i;
if(idx2>=0) r= min(r,i-idx2);
}else if(ws[i]==w2){
idx2=i;
if(idx1>=0) r= min(r,i-idx1);
}
}
return r;
}https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/20887/12-16-lines-java-c
 Follow up:
Follow up:
- minimum window substring
三个单词的距离就是最小的window含有三个给定的单词.
比如下面是一个句子,三个单词是a,b,c, 最短的距离应该是4.
a k b d [a c g b] e f a d s f [b c g a]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17这个是minimum substring window的简化版本 array
map<string,int> + two pointers即可搞定.
m[a]=0,4,10,17
m[b]=2,7,14
m[c]=5,15就用minimum substring window sliding window的做法.
vector<string> vs={"ax","k","b","d","ax","c","g","b","e",
"f","ax","d","s","f","b","c","g","ax"};
vector<string> t={"ax","c","g","b"};
int shortestdistanceoftriplet(VS& ws, VS& t){
unordered_map<string, int> m;
int count=0, r=0x7fffffff;
for(int i=0;i<t.size();++i) m[t[i]]++;
count = m.size();
for(int i=0, j=0;i<ws.size();++i){
if(m.count(ws[i])==0) continue;
while(count!=0 && j<ws.size()){////
if(m.count(ws[j])>0) {
m[ws[j]]--;
if(m[ws[j]]==0) count--;
}
j++;
}
if(count==0) r=min(j-i,r);
if(m[ws[i]]==0) count++;
m[ws[i]]++;
}
return r;
}
52.9 Maximum product of a triplet
Input: [10, 3, 5, 6, 20]
Output: 1200
Input: [-10, -3, -5, -6, -20]
Output: -90
Input: [1, -4, 3, -6, 7, 0]
Output: 168如图红正绿负.通过观察找规律,可以看出MaxProductOfThree一定是等于: max(max1*max2*max, min1*min2*max1).
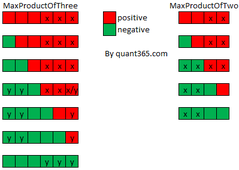
时间复杂度: \(O(N)\), 空间复杂度: \(O(1)\)
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-maximum-product-of-a-triplet-in-array/
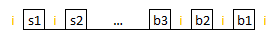
int solution(vector<int> &A) {
if (A.size() < 3) return -1;
//smallest 1st, 2nd;biggest 1st, 2nd, 3rd
int s1=INT_MAX, s2=INT_MAX, b1=INT_MIN, b2=INT_MIN, b3=INT_MIN;
for(int i: A){
if(i>b1) b3=b2,b2=b1,b1=i;
else if(i>b2) b3=b2,b2=i;
else if(i>b3) b3=i;
if(i<s1) s2=s1,s1=i;
else if(i<s2) s2=i;
}
return max(s1*s2*b1, b1*b2*b3);
}这道题牵扯到在一个无序数列中找最大的前三和最小的前二,如果要求最小的比较数目,可以用tournament tree. Please refer to: linkedin-2017-01.html#tournament-tree
import java.math.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
// Given an array of integers, return the highest product possible by multiplying 3 numbers from the array
public int maxp3(ArrayList<Integer> A) {
if(A.size()<3) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/*
// Array.sort
Collections.sort(A); // non-descending order O(NLogN)
int L=A.length();
// max1 x max2 x max3
// min1 x min2 x max1
return Math.max(A.get(L-1)*A.get(L-2)*A.get(L-3), A.get(0)*A.get(1)*A.get(L-1));*/
int mx1=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int mx2=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int mx3=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int mi1=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int mi2=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i: A){
if(i>mx1) {mx3=mx2; mx2=mx1; mx1=i;}
else if(i>mx2){mx3=mx2; mx2=i;}
else if(i>mx3){mx3=i;}
if(i<mi1) {mi2=mi1; mi1=i;}
else if (i<mi2){ mi2=i;}
}
return Math.max(mx1*mx2*mx3, mx1*mi1*mi2);
}
public static void main(String []argv){
Solution sln=new Solution();
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(-3,4,5,6));
System.out.println(sln.maxp3(al));
}
}52.10 Median/Max/Min Stack
对midstack来说, popMedian()可以做到\(O(1)\). 如果是maxstack, minstack, popMin/Max和普通的pop()不可能同时做到\(O(1)\).
例如push 1,3,6,5,4. 返回6.返回index的中值. 双链表做,maintain一个pointer指向中间
follow up是写popMid()函数
Solution: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/design-a-stack-with-find-middle-operation/.
如果不要求popMedian常数时间,可以用vector实现. 如果popMedian要O(1),必须要linked list.
自己实现了一个返回Lower Median的midstack. 注意:
Change mid pointer in two cases: 1) Linked List is empty 2) Number of nodes in linked list is odd
stack为空的时候peekmedian返回一个特殊值,popmedian不做任何操作.
struct midstack {
list<int> stk;
list<int>::iterator it;
int top() { return stk.back(); }
void push(int i) {
stk.push_back(i);
if (stk.size() == 1)
it = stk.begin();
else if (stk.size()&1)
it++;
}
void pop() {
stk.pop_back();
if (stk.size() && ((stk.size() & 1) == 0))
it--;
}
//O(1) - empty return INT_MIN
int peek_median() {
if (stk.empty()) return INT_MIN;
return *it;
}
//O(1)
void pop_median() { if(!stk.empty())stk.erase(it); }
};这个是纯手工的非STL版本: Design a stack with operations on middle element: http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/design-a-stack-with-find-middle-operation/
https://www.glassdoor.com/Interview/How-do-you-find-the-middle-of-a-stack-at-O-1-QTN_1096333.htm
52.10.1 MaxStack

http://wxx5433.github.io/max-stack.html
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class MaxStack<T> {
LinkedList<T> stack;
PriorityQueue<T> maxHeap;
public MaxStack() {
stack = new LinkedList<T>();
maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<T>(10, Collections.reverseOrder()); // reverse order
}
public void push(T n) {
stack.addLast(n);
maxHeap.offer(n);
}
public T pop() {
T num = stack.removeLast();
maxHeap.remove(num);
return num;
}
public T top() {
return stack.peekLast();
}
public T peekMax() {
return maxHeap.peek();
}
public T popMax() {
T num = maxHeap.poll();
stack.remove(num);
return num;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxStack<Integer> stack = new MaxStack<Integer>();
int[] arr = {3, 1, 2, 4, 6, 5};
for (Integer n: arr) {
stack.push(n);
}
System.out.println(stack.popMax()); // 6
System.out.println(stack.popMax()); // 5
System.out.println(stack.popMax()); // 4
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 2
System.out.println(stack.popMax()); // 3
}
}Complexity:
push, pop, top: \(O(logn)\)
peekMax: \(O(1)\)
popMax: \(O(logN)\) - 原来网页的复杂度是错误的!
普通的pop其实他没有问,但是我也写了一个给他.后来他说他见过的最clean的办法是用一个
包含index和max的数据结构来做,但是没细说…反正我这轮过了,估计只要说出两个堆一起用差不多就行了
http://www.1point3acres.com/bbs/forum.php?mod=redirect&goto=findpost&ptid=106359&pid=1472407&fromuid=91137
假设数据value没有重复,可以用下面的数据结构:
list<int> stk;
list<list<int>::iterator> max_itr;
map<int,list<list<int>::iterator>::iterator> val2itr;map to list<list<int>::iterator>::iterator is better to map to list<int>::iterator here!!! Why? list erase and remove difference!!
push()复杂度是\(O(N)\),pop()和popmax()的复杂度都是\(O(1)\).
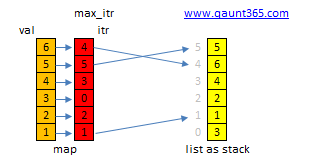
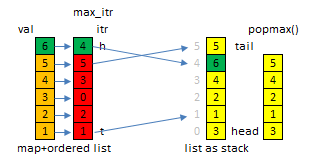
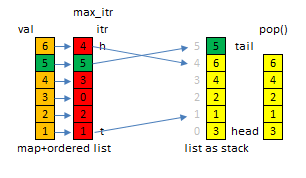
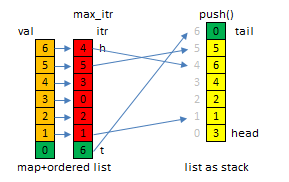
struct maxstack {
list<int> stk;
list<list<int>::iterator> max_itr;
unordered_map<int, list<list<int>::iterator>::iterator> val2itr;
void push(int i) {// O(N) average
stk.push_back(i);
auto tmp = stk.end();
--tmp;
for (auto it = max_itr.begin(); it != max_itr.end(); ++it) {
if (**it < i) {
auto nit = max_itr.insert(it, tmp);
val2itr[i] = nit;
return;
}
}
max_itr.push_back(tmp);
val2itr[i] = max_itr.end();
--val2itr[i];
}
int pop() { // O(1) average
if (stk.empty()) return INT_MIN;
int val = stk.back();
max_itr.erase(val2itr[val]); // cannot use remove
val2itr.erase(val);
stk.pop_back();
return val;
}
int popmax() { // O(1) average
if (stk.empty()) return INT_MIN;
list<int>::iterator m = max_itr.front();
int r = *m;
val2itr.erase(r);
stk.erase(m);
max_itr.pop_front();
return r;
}
};- How to get iterator to last element in std::list?
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2678175/iterator-to-last-element-in-stdlist
52.13 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
无环:
 https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
A: a1 → a2
\
c1 → c2 → c3
/
B: b1 → b2 → b3begin to intersect at node c1.
Notes:
If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
This takes \(O(M+N)\) time and \(O(1)\) space, where M and N are the total length of the linked lists. Maybe inefficient if the common part is very long (i.e. M,N >> m,n)
Traverse the two linked list to find M and N.
Get back to the heads, then traverse |M − N| nodes on the longer list.
Now walk in lock step and compare the nodes until you found the common ones.
struct Solution {// 39ms, 80%
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if (!headA || !headB) return nullptr;
int c1=0, c2=0;
ListNode *a= headA, *b =headB;
while(a->next){c1++, a=a->next;}
while(b->next){c2++, b=b->next;}
if (a!=b) return nullptr;
int d = abs(c1-c2);
while(d--)
if (c1>c2) headA = headA->next; else headB = headB->next;
while(headA!=headB)
headA = headA->next, headB = headB->next;
return headA;
}
};看到另外一种解法One pass更快,但是太tricky,不推荐,而且如果没有交叉,那么会陷入死循环.作为参考请看:http://www.jianshu.com/p/6b38199dac15
class Solution { // 35ms, 90% leetcode有bug,没有交叉会死循环
public:
ListNode* getIntersectionNode(ListNode* headA, ListNode* headB) {
if(!headA || !headB) return NULL;
ListNode *listA = headA, *listB = headB;
while(listA && listB){
if(listA == listB) return listA;
listA = listA -> next;
listB = listB -> next;
if(listA == listB) return listA;
if(listA == NULL) listA = headB;
if(listB == NULL) listB = headA;
}
return listA;
}
};http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2014/12/04/leetcode-intersection-two-linked-lists/
- 无环不相交 2. 无环相交. 3. 有环不相交. 4. 有环相交
Leetcode的题目没有考虑Cyclic Linked List 3,4两种情况.
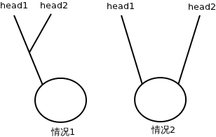
自己画的,双圆圈表示交点.一种交在环上,一种交在尾巴上.
个人总结,要明白以下几点:
无环链表和有环链表是不可能相交的;
两个有环链表若相交,其“整个环上”的所有node一定都重合;
有环链表的相交,情况只有2种:相交于“环上”或相交于“不是环的部分”,即下图所示;两种情况都需要使用“两个指针的追逐”方法来判断两个链表的环部分是否相交; 带环单向链表相交只有2种情况
有关链表追逐的考虑: 相对速度、距离、时间要算好,否则很容易漏掉几种边界情况;
- 用快慢指针判断是否有采用
Floyd's Tortoise and hare(Floyd龟兔赛跑)算法
参考: linked-list, 不过那道题我们返回bool,这里返回的是Node*.
Node* has_circle(Node* head) {
Node *h=head, *t=head;
while (h && t && t->next) {
h = h->next, t = t->next->next;
if (h == t) return h;
}
return NULL;
} https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-i
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-i
 https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii
比leetcode还要generic的版本.应该用手写出来:
int is_intersected(Node* p1, Node* p2) {
Node* has_circle_1 = has_circle(p1);
Node* has_circle_2 = has_circle(p2);
if (has_circle_1) {
if (has_circle_2) {
//如果两个都有环,那么两个返回的点都在环上,则用快慢指针相遇的方法
Node* pp1 = has_circle_1;
Node* pp2 = has_circle_2;
if (pp1 == pp2 || pp1->next == pp2)
return 1;
while (pp1->next != has_circle_1) { //pp1转一圈,注意while的条件
pp1 = pp1->next;
pp2 = pp2->next->next;
if (pp1 == pp2)
return 1;
}
return 0;
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
if (has_circle_2) {
return 0;
} else {
while (p1->next) p1 = p1->next;
while (p2->next) p2 = p2->next;
return p1 == p2;
}
}
return 0;
}http://pfmiles.github.io/blog/algorithms-in-job-interview-test-if-two-linked-lists-intersected/
https://charleshm.gitbooks.io/leetcode/content/lian_biao_cheng_huan.html
https://my.oschina.net/acidsweet1990/blog/260852
 上面只是判断了有环是否相交,那么如果相交,有环的情况下如何找交点呢?
上面只是判断了有环是否相交,那么如果相交,有环的情况下如何找交点呢?
对于有环在环上相交的情况,其实两个交点都是交点.
对于有环在尾巴上相交的情况,随便在环上找一个点,然后和无环相交的情况相同的算法可解.
52.14 50. Pow(x, n)
 https://leetcode.com/problems/powx-n/
https://leetcode.com/problems/powx-n/
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/write-a-c-program-to-calculate-powxn/
52.14.1 递归(Recusive)
Method: Divide and Conquer + Memorization + Recursive
用recursive把负数的问题变为正数,用DC把问题解决,用memorization实现复杂度优化\(O(LogN)\)
T: \(O(LogN)\) S: \(O(LogN)\)
52.14.2 Iterative
T: \(O(LogN)\) S: \(O(1)\)
The recursive solutions are generally not preferred as they require space on call stack and they involve function call overhead.
这种做法如何理解呢?加入 n = 13,13在二进制中表示为:00001101,那么\(13 = 2^3 + 2^2 + 2^0\)
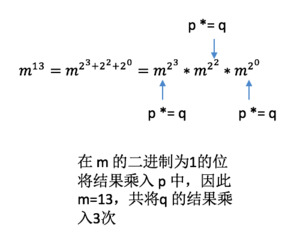
double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(x==1.0 || x==0) return x;
int m = (n<0) ? -(n+1) : n; //-(INT_MIN+1) == INT_MAX
double p = 1.0, y=x;
while (m){
if (m&1) p*=y; // 1
y*=y, m>>=1;
}
return (n<0)?(1/p/x):p;
}比如输入是myPow(2.0, 13):
p y m
p*=(2.0) , m = 13
(2.0)^2 , m = 6
p*=(2.0)^4 , m = 3
p*=(2.0)^8 , m = 1
- , m = 0方法是:
m每次减半,m是偶数的时候y翻倍(square),m是奇数的时候,把y的值计入最终结果p*=y.
Another Explanation: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/25571377/iterative-implementation-of-powx-n
52.15 Hangman Game
Check: system-design
52.16 K Closest Points(KNN)
找N个点里面离origin最近的K个点.计算几何里面的经典问题.K-d Tree的典型应用. 下面是点point的定义:
很多种算法可解这个题,下面列举4种:
52.16.1 1. Priority Queue
构造函数API: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/priority_queue/priority_queue
- minheap
minheap是对所有N个点创建一个heap,然后pop出K-1个点,剩下的PQ的top即为答案.复杂度是T:\(O(N+KLogN)\), S: \(O(N)\)
注意 how to write priority_queue with a custom comparator.
struct comp {
bool operator()(point& l, point& r){
return (l.x*l.x + l.y*l.y) > (r.x*r.x + r.y*r.y);
}
};
// O(N+KLogN) minheap
point knn(vector<point>& ps, int k) {
point dummy={INT_MIN,INT_MIN};
if (ps.size() <= k || k<=0) return dummy;
priority_queue<point, vector<point>, comp> pq(comp(), ps); // O(N)
while (--k) pq.pop(); // O(KLogN)
return pq.top();
}注意推荐在constructor构建PQ,可以做到\(O(N)\). 不要通过插入的方式构建PQ,那样是\(O(NlogN)\).(见CLRS P166)
// 错误的方式 O(NLogN + KLogN) == O((N+K)LogN) minheap - Bad implementation
point knn(vector<point>& ps, int k) {
if (ps.size() <= k || k<=0) return {INT_MIN,INT_MIN};
priority_queue<point, vector<point>, comp> pq;
for (int i = 0; i < ps.size(); ++i) pq.push(ps[i]);
while (--k) pq.pop();
return pq.top();
}- maxheap
maxheap是建立一个大小为K的maxheap,root是heap中的最大值,然后继续拿剩余的点(比如叫做点p)和root比较,如果比root大就continue继续下一个,如果比root小就弹出root,插入p.复杂度是T:\(O(K+(N-K)LogK)\), S:\(O(K)\)
// O(K+(N-K)LogK) maxheap
point knn(vector<point>& ps, int k) {
point dummy = { INT_MIN,INT_MIN };
if (ps.size() <= k || k <= 0) return dummy;
auto COMP= [](const point&l, const point& r) {
return (l.x*l.x + l.y*l.y) < (r.x*r.x + r.y*r.y);
};
//priority_queue< point, vector<point>, decltype(COMP)> pq(COMP);
int i = 0;
priority_queue< point, vector<point>, decltype(COMP)>
pq(ps.begin(), ps.begin() + k, COMP); // O(K) - 注意构建方式
int i = k;
while (i++ < ps.size()) // (N-K)LogK
if (COMP(ps[i], pq.top())) { pq.pop(), pq.push(ps[i]); }
return pq.top();
} which one is better
which one is better
这里把N,K都看成变量,所以在复杂度公式中不能省去.
minheap和maxheap到底哪一个在实际中更快呢? 其实就是比较\(O(N+KLogN)\)和\(O(K+(N-K)LogK)\). \(log(x)\)是在这两个复杂度公式里面起主导作用的函数,如果N很大,那个用\(LogN\)那个肯定更快; 如果K很大,那么LogK那个肯定更快(推到极限如果N==K,肯定maxheap快).
我们可以做一个简单的运算来印证一下(因为复杂度里面的log是不看base的,所以2为底还是e为底没关系):
>>> n=10000
>>> k=500
>>> n+k*math.log(n)
14605.170185988092
>>> k+(n-k)*math.log(k)
59538.77693501082
>>> k=9000
>>> n+k*math.log(n)
92893.06334778565
>>> k+(n-k)*math.log(k)
18104.979856318358All in all,如果K相对N较小,第一种方法minheap其实更好; 如果K比较大,那么第二种方法maxheap更好.
52.16.2 2. QuickSelect
Another approach (instead of Minimum Heaps) is to use the median of medians select to find the k-th closest point to the origin and then iterate through the entire array and print k points which are closer/as close as the k-th closest point (to avoid missing some points in case there are several points as close as the k-th point, we might need two passes on the points array).
If we are allowed to change the original points array then this solution is O(n) run-time complexity and O(1) space complexity. If not then the space complexity is O(n).
// nth_element - O(N)
point knn(vector<point>& ps, int k) { // O(N)
if (ps.size() <= k) return {INT_MIN,INT_MIN};
nth_element(ps.begin(), ps.begin() + k - 1, ps.end(),
[](point& p1, point& p2) {
return (p1.x*p1.x + p1.y*p1.y) < (p2.x*p2.x + p2.y*p2.y);
});
return ps[k - 1];
}n_element直接解题,注意函数的signature.
Selection Algorithm: 平均 \(O(N)\), 最差 \(O(N^2)\). 根据:http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/algorithm/nth_element, n_element的平均复杂度明确是\(O(N)\),但是最差是\(O(N^2)\).
STL n_element source code:
// TEMPLATE FUNCTION nth_element WITH PRED
template<class _RanIt,
class _Pr> inline
void _Nth_element_unchecked(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Nth, _RanIt _Last, _Pr& _Pred)
{ // order Nth element, using _Pred
if (_Nth == _Last)
return; // nothing to do
for (; _ISORT_MAX < _Last - _First; )
{ // divide and conquer, ordering partition containing Nth
pair<_RanIt, _RanIt> _Mid =
_Partition_by_median_guess_unchecked(_First, _Last, _Pred);
if (_Mid.second <= _Nth)
_First = _Mid.second;
else if (_Mid.first <= _Nth)
return; // Nth inside fat pivot, done
else
_Last = _Mid.first;
}
_Insertion_sort_unchecked(_First, _Last, _Pred); // sort any remainder
}想让最差是\(O(N)\)的话需要用median of median算法: https://interviewalgorithm.wordpress.com/sortingordering/median-of-medians-algorithm/
One can assure linear performance even in the worst case by using a more sophisticated pivot strategy; this is done in the
median of medians algorithm. However, the overhead of computing the pivot is high, and thus this is generally not used in practice. One can combine basic quickselect with median of medians as fallback to get both fast average case performance and linear worst-case performance; this is done inintroselect.
52.16.3 3. Kd Tree
Kd树的典型应用之一就是Nearest neighbour search(参见:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/K-d_tree#Nearest_neighbour_search).
If we have a set of points and a lot of queries , where start point , K change, maybe it is better to use Kd tree for 2d. With Kd tree time complexity is \(KLog(N)\) for query and \(NLog(N)\) for building the tree.Space complexity \(O(N)\).With Kd tree we don’t need even to calculate euclidean distance
Finding the nearest point is an O(log n) operation in the case of randomly distributed points, although analysis in general is tricky. However an algorithm has been given that claims guaranteed O(log n) complexity.[9]
52.16.4 4. RTree
//TODO
http://www.sai.msu.su/~megera/postgres/talks/pgcon-2010-1.pdf
现实应用:
- Scikit:
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/neighbors.html#k-d-tree
- Alglib
http://www.alglib.net/other/nearestneighbors.php
- PostGIS
http://workshops.boundlessgeo.com/postgis-intro/knn.html
“KNN” stands for “K nearest neighbours”, where “K” is the number of neighbours you are looking for.
KNN is a pure index based nearest neighbour search. By walking up and down the index, the search can find the nearest candidate geometries without using any magical search radius numbers, so the technique is suitable and high performance even for very large tables with highly variable data densities.
The KNN system works by evaluating distances between bounding boxes inside the PostGIS
R-Treeindex.
参考:
https://shepherdyuan.wordpress.com/2014/07/23/linkedin-k-closest-points/
http://www.zrzahid.com/k-closest-points/
https://www.careercup.com/question?id=4751976126480384
相关的leetcode题目是这一道:
52.16.5 215. Kth Largest Element in an Array
 https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
struct Solution { // T:O(N) S:O(1)
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {// [1], 1
nth_element(nums.begin(), nums.begin()+k-1, nums.end(), [](int x,int y){return x>y;});
return nums[k-1];
}
};注意第k大的元素的index是k-1.
GFG上面也有2道题目和这个类似:
- Closest Pair of Points
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/closest-pair-of-points-onlogn-implementation/
- Find k closest elements to a given value
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-k-closest-elements-given-value/
52.17 450. Delete Node in a BST
 https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
There could be multiple ways to solve. Why OJ only check one possibility? e.g., 2,1,3 tree, delete 2, I can have 1,null,3 or 3,1. Both solutions are valid.
因为要delete,在find这个node的过程中要保留一个parent的变量
被删除的node有三种情况:没孩子(leaf),一个孩子,两个孩子(最麻烦)
分析:假设当前node 为root
if value < root.val, 要被删除的节点在左子树,往左子树递归,并把操作结束后的返回值作为新的root.left
if value > root.val, 要被删除的节点在右子树,往右子树递归, 并把操作结束后的返回值作为新的root.right
if root == null, 递归到了一个null点,说明要删的value不存在,return null,而这个null点的parent的相应子树本来也是null,对树的结构没有任何影响
if value == root.val,说明root是该被删除的了
A. if root.left == null, return root.right
B. if root.right == null, return root.left(这两个case其实包含了只有一个child和一个child都没有的三种情况)
C. 如果两个children都存在,从右子树中找最小的node,与root交换,再递归调用函数在右子树中删除root.val
public struct Solution {
public TreeNode removeNode(TreeNode root, int value) {
// write your code here
if (root == null) return null;
if (value < root.val)
root.left = removeNode(root.left, value);
else if (value > root.val)
root.right = removeNode(root.right, value);
else {
if (root.left == null) return root.right;
if (root.right == null) return root.left;
TreeNode minOfRight = findMin(root.right);
//swap root and minOfRight
int temp = root.val;
root.val = minOfRight.val;
minOfRight.val = temp;
root.right = removeNode(root.right, minOfRight.val);
}
return root;
}
public TreeNode findMin(TreeNode cur) {
while (cur.left != null) {
cur = cur.left;
}
return cur;
}
}http://algorithms.tutorialhorizon.com/binary-search-tree-complete-implementation/
52.18 Lazy caterer’s sequence and Cake number
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lazy_caterer's_sequence

Check this animation
在切第n刀的时候 最多能和之前的n-1刀相交 这个多出来的1刀多制造出了n块pizza.So就是dp[1] = 1, dp[n] = dp[n - 1] + n, 公式应该是 \(\frac{n(n + 1)}{2} + 1\).
52.19 78. Subsets I II
 https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
 https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
主要是聊算法复杂度上的东西,要不要排序,排序的好处坏处是什么.
52.20 464. Can I Win (if I go first)
In the “100 game,” two players take turns adding, to a running total, any integer from 1..10. The player who first causes the running total to reach or exceed 100 wins.
What if we change the game so that players cannot re-use integers?
For example, two players might take turns drawing from a common pool of numbers of 1..15 without replacement until they reach a total >= 100.
Given an integer maxChoosableInteger and another integer desiredTotal, determine if the first player to move can force a win, assuming both players play optimally.
You can always assume that maxChoosableInteger will not be larger than 20 and desiredTotal will not be larger than 300.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/can-i-win/
https://leetcode.com/problems/can-i-win/
http://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/53266731
重要条件:
You can always assume that maxChoosableInteger will not be larger than 20 and desiredTotal will not be larger than 300.
每个人开始前都不能选前面已经用过的数字!
分析:
The solution is quite strightforward. First off we have to eliminate primitive cases. So,
if the first player can choose a number, which is already greater than or equal to the desired total obviously it wins.
If max choosable integer is less than the desired total, but if it exceeds the desired total in sum with any other number then the first player loses anyway.
If the sum of all number in the pool cannot exceed or reach the desired total, then no one can win.
Now, for the other cases we can use MiniMax logic to reveal the winner. Because both player play optimally, In order to win, the first player has to make a choice, that leaves the second player no chance to win. Thus, at each step we consider all the possible choices by the current player and give turn to the second player recursively. If we find a move, after which the second player loses anyway or we have already exceed the desired total by adding the chosen number, we return true, i.e the current player wins. This way the game looks like the following tree:
player1 -> 0
/| ...\
player2 -> 1 2 ....max
/|\ ..../ | \
player1 -> 2 3... 1 2 ..max-1
... \
player1 -> / | \ lose
player2 -> lose win loseThe figure above helps to imagine how the algorithm considers all possible scenarios of the game. The leafs of the game tree are lose or win states for one of the players. Finally the logic concludes to the idea, that if some branch does not contain any leaf that ends with win state for player2, the move associated with that branch is the optimal one for the first player.
P.S: Time complexity of naive implementation will work for \(O(N!)\). Therefore we have to memorize branch states after traversing once.
例子:
(5,12) is true! 注意这里是采用最优策略走会赢,如果乱走还是会输. 如下图:
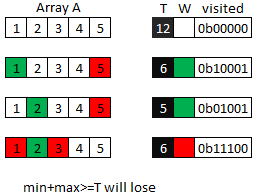
如果红先绿后,红如果第一次选5,是必然输的. The guaranteed win actually comes when Player 1 chooses 3 first:
3-1-2 {4,5} left for p2 to choose. Either way player 1 wins
3-2-1- {4,5} left for p2 to choose. Either way player 1 wins
3-4-5. P1 wins
3-5-4. P1 wins代码:
struct Solution { // 109 ms, beat 89%
bool miniMax(int state, unordered_map<int,bool> &dp, int goal, int maxn){
if(dp.count(state)) return dp[state];//该状态已经被搜索过
for(int i=maxn-1; i>=0; i--)//遍历每个数字
if(state&(1<<i)) //如果它还没被使用getbit(i)==1
//如果当前已经能实现目标,或对方接下来不能赢.(异或把该位变0表示使用该数字)
if(i+1>=goal || !miniMax(state^(1<<i),dp,goal-i-1,maxn)) return dp[state] = true;
return dp[state] = false;
}
bool canIWin(int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal){
if(maxChoosableInteger>=desiredTotal) return true;
if(maxChoosableInteger*(maxChoosableInteger+1)/2<desiredTotal) return false;
int state = (1 << maxChoosableInteger) - 1; //初始状态为全1即全部数字都可用(1==available)
unordered_map<int,bool> dp(desiredTotal);//记录状态,dp[i]表示当前可用数为i,目标为goal时能不能赢
return miniMax(state, dp, desiredTotal, maxChoosableInteger);
}
};二刷:
struct Solution {
bool canIWin(int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal) {
if(maxChoosableInteger>=desiredTotal) return true;
if(maxChoosableInteger*(maxChoosableInteger+1)/2 < desiredTotal) return false;
int state = (1 << maxChoosableInteger) - 1;
unordered_map<int, bool> dp(desiredTotal);
return dfs(state,dp,maxChoosableInteger,desiredTotal);
}
bool dfs(int state,unordered_map<int, bool>& dp,int mx,int g){
if(dp.count(state)) return dp[state];
for(int i=1;i<=mx;++i){
if(state & (1<<(i-1))){
if(i>=g || !dfs(state^(1<<(i-1)),dp,mx,g-i)) return dp[state]=true;
}
}
return dp[state]=false;
}优化:
因为maxChoosableInteger will not be larger than 20,状态数量不会超过1M(\(2^{20}\)),所以unordered_map<int,bool>可以被优化为vector,int可以直接用vector index来表示.状态映射的值有三种情况: 0-unvisited, 1-win, 2-lose.
struct Solution { // 26 ms, Your runtime beats 97.17% of cpp submissions.
vector<char> cache;
int state, maxInt;
bool canIWin(int maxChoosableInteger, int desiredTotal) {
int sum = maxChoosableInteger * (maxChoosableInteger + 1) / 2;
if (sum < desiredTotal) return false;
if (desiredTotal <= 0) return true;
maxInt = maxChoosableInteger;
state = 0;
cache = vector<char>(1<<maxChoosableInteger,0);//0-unvisited, 1-win, 2-lose
return miniMax(desiredTotal);
}
bool miniMax(int desiredTotal) {
if (desiredTotal <= 0) return false; //!!
if (cache[state]) return cache[state]==1;
int mask = 1;
for (int i=0; i<maxInt; ++i) {
if (!(state & mask)) {
state |= mask;
if (!miniMax(desiredTotal-i-1)) {
state &= ~mask;
return cache[state] = 1;
}
state &= ~mask;
}
mask <<= 1;
}
cache[state] = 2;
return false;
}
};reference: https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/68896/java-solution-using-hashmap-with-detailed-explanation/11
复杂度:
因为DP每个状态都要检查一下,得到一个状态最多循环N次,所以是\(O(N*2^N)\), N = maxChoosableInteger.
Time complexity of naive implementation is \(O(N!)\).
How to prove \(N! > N*2^N\):
\[ N!=1*2*3*4*5*6...*N \\ N*2^N=2*2*2*2*2*2...2*N \]
52.21 297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
 https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
 follow up是如何序列化和反序列化Graph,如果有环怎么办.
follow up是如何序列化和反序列化Graph,如果有环怎么办.
52.22 449. Serialize and Deserialize BST
 https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-bst/
https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-bst/
上周面的LinkedIn,今天HR 打电话过来说我面得还行,但是是border line, 他们 hiring committee讨论了很长时间最终决定把我拒了,心情很难受,听到" unfortunately"的那一刻眼泪流出来.
把面试过程写出来,请过来人帮我看看.HR 说我主要是System Design 和coding 面的 不完美.其实题目都不难,面经和leetcode 上的题
System Design:LinkedIn有个share功能,在里面会出现一些URL,问题是找出在过去 一天,一小时,五分钟被share的top 5/10/…多的URL.
这个面的感觉有点窝囊,感觉再让我面一次一定说的更好,我是按照july那个帖子来说 的,先把这些url 的id hash一下 (总共1 million url 所以可以存到一张表里),然后 用kafka (Producer and Consumer),隔一段时间(这样可以减少IO)根据hash 结果 存到不同机器上做aggregation, 为了节省计算量,可以每一分钟一张表存frequency ,然后把这些表加起来用priority queue排序就行了(这是5分钟的情况), 还可以提到 中间可以缓存加cache, 还提到了consistency hashing,感觉关键点都说出来了(也许 不对?).可是面试官明明都点头的啊.
总体有点乱,我刚开始还只是一个high level solution呢,但我每提一个step面试官 就打断我问细节,有种被人不停push 加捣乱的感觉,加上白板有点小,画的有点乱, 自己阵脚也乱了.
Coding 1 : isomorphic string; serialize and deserialize Binary Tree
Coding 2:Sqrt(double x, double e), e为一个小数允许误差范围; Find leaves
除了sqrt我都是一次写出完美代码的, sqrt我之前只准备了integer的那个版本,现场 临时想double 还要小数范围废了点时间,主要用在clarification 上,刚开始 misunderstanding以为他要精确到0.01了,另外我还忘了\(0<x<1\)的情况,后来经提示才 补充上去.另外isomophic string 的follow up, 要讨论一组数的情况,开始没领会面 试官的意思,废了点时间communication.
其实都是小中面试官,估计年龄都没有我大,只有一个小印shadow, 面试前一天刚看到 hr给我发的邮件上除了hosting Mgr都是中国人的时候还挺高兴,心想至少不会被烙印 阴了,好好面就行.
Lz在别的州工作好几年,现在这个公司干的不开心,另外也为了到加州来可以让一家人 生活在一起,结束目前一家三口在三个地方生活的悲惨日子…其实linkedin是个很 好的公司, 至少口碑很好,我也是用心准备的.Lz时间有限,平时下班回家就刷题, 差不多刷了两遍,断了所有的社交,最近几个月工作也没有努力因为把所有空闲时间加 上一部分上班时间都 用来刷题了.因为在外州,面试需要请假,没有申请很多公司,目前面的都是hr在 linkedin上直接联系我的那种. 现在的状况是几个月前fail掉亚麻(那时候才刚刚开 始,coding和behavior都没有面好,fail掉不奇怪);9月 Ms家两轮电面后没有下文; GF这样的公司还没有敢去申请,.马上就要感恩节圣诞节了,好心塞 http://www.mitbbs.com/article_t/JobHunting/33246829.html
http://massivealgorithms.blogspot.com/2015/12/linkedin-interview-misc-2.html
52.23 341. Flatten Nested List Iterator
52.24 Isomorphic String
 https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
有点像找对象,男女双方都不能找两个,必须严格一对一. 两个map搞定.
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if(s.size() != t.size()) return false;
map<char, char> m;
map<char, char> m2;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(m.count(s[i])){
if(t[i] != m[s[i]]) return false;
if(m2[m[s[i]]] != s[i]) return false;
}else{
if(m2.count(t[i])) return false;
m[s[i]] = t[i];
m2[t[i]] = s[i];
}
}
return true;// empty - empty => true
}仔细想想发现第二个map可以改为用一个bitset代替,如果是新男,而对应的是旧女,就return false.
struct Solution {
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if(s.size()!=t.size()) return false;
map<char,char> m;
bool b[256]={false};
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(m.count(s[i])==0){ // s[i] new item
if(b[t[i]]) return false;
m[s[i]] = t[i], b[t[i]]=true;
}else{
if(m[s[i]]!=t[i])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};数学上这叫bijection. 由于问题的对称性,可以男女分别检查一遍.这样写:
struct Solution {
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if(s.size()!=t.size()) return false;
return jection(s,t) && jection(t,s);
}
bool jection(string &s, string& t){
map<char,char> m;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(m.count(s[i])==0){ // s[i] new item
m[s[i]] = t[i];
}else{
if(m[s[i]]!=t[i])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}; follow up是给一堆string, 按组输出isomorphic strings, 输出格式是List<List
follow up是给一堆string, 按组输出isomorphic strings, 输出格式是List<List
https://www.jiuzhang.com/qa/2521/
public List<List<String>> IsomorphicString(List list) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : list) {
char pointer = 'A';
char[] pattern = new char[256];
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
if (pattern[(int)c] == 0) {
pattern[(int)c] = pointer++;
}
}
String p = buildPattern(pattern, str);
if (!map.containsKey(p)) {
map.put(p, new ArrayList());
}
map.get(p).add(str);
}
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
result.add(map.get(key));
}
return result;
}
public String buildPattern(char[] pattern, String str) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {
sb.append(pattern[(int)c]);
}
return sb.toString();
}2016-11-01 张助教 想法是对的. 但是你这个程序是可以优化的,匹配的这个部分,你是用map做的,在数据量非常大的情况下可以考虑用字典树来处理.
52.27 Union and Intersection of two Linked Lists
http://www.1point3acres.com/bbs/thread-214086-1-1.html
如果list是unsorted的,需要一个hashtable.O(M+N).不然O(M*N).
参考:http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/union-and-intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
If both lists are unsorted. T: \(O(M*N)\)
bool ispresent(struct node *head,int data){
while(head!=NULL){
if(head->data==data) return true;
head=head->next;
}
return false;
}
void unionlist(struct node *a,struct node *b){
struct node *union1=NULL;
struct node *head1=a;
while(a){
push(&union1,a->data);
a=a->next;
}
while(b){
if(!ispresent(head1,b->data)) push(&union1,b->data);
b=b->next;
}
}
void interlist(struct node *a,struct node *b){
struct node *inter=NULL;
while(a){
if(ispresent(b,a->data)) push(&inter,a->data);
a=a->next;
}
}If both lists are sorted. T: \(O(min(M,N))\)
Alog1:
void unionlist(struct node *a,struct node *b){
struct node *union1=NULL;
while(a&&b) {
if(a->data < b->data) {
push(&union1,a->data);
a=a->next;
} else if(a->data > b->data) {
push(&union1,b->data);
b=b->next;
} else {
push(&union1,a->data);
a=a->next, b=b->next;
}
}
while(a) push(&union1,a->data), a=a->next;
while(b) push(&union1,b->data), b=b->next;
}
void interlist(struct node *a,struct node *b){
struct node *inter=NULL;
while(a&&b){
if(a->data < b->data)
a=a->next;
else if(a->data > b->data)
b=b->next;
else{
push(&inter,a->data);
a=a->next, b=b->next;
}
}
}Algo2:
void unionlist_hash(struct node *a,struct node *b){
map<int,struct node *> m;//hashtable
struct node *union1=NULL;
while(a){
push(&union1,a->data);
m[a->data]=a;
a=a->next;
}
while(b){
if(m.find(b->data)==m.end())
push(&union1,b->data);
b=b->next;
}
}
void interlist_hash(struct node *a,struct node *b){
map <int,struct node *> m;
struct node *inter=NULL;
while(a){
m[a->data]=a;
a=a->next;
}
while(b){
if(m.find(b->data)!=m.end())
push(&inter,b->data);
b=b->next;
}
}