Chapter 29 Palindrome
这个专题讨论所有和palindrome相关的问题.
- pal is an abbreviation of Palindrome in this section.
LPS - Longest Palindromic Subsequence
LPs - Longest Palindromic Substring
LCS - Longest Common Subsequence
LCs - Longest Common substring
问题可以是求长度,个数,或者求所有满足条件的结果.
https://leetcode.com/problemset/all/?search=palindrom
29.1 isPalindrome(ispal)
This should be done in ten seconds.
bool ispal(const string & s, int h, int t){ // like reverse string
while(h<t) if (s[h++]!=s[t--]) return false; // two steps per loop
return h<=t; // empty string return true
}
bool ispal(const string& s){ // logic applied to empty string too
int h = 0, t=s.size()-1;
while(h<t) if (s[h++]!=s[t--]) return false; // two steps per loop
return true;
}29.2 Valid Palindrome with Space
Given a string, determine if it is a palindrome, considering only alphanumeric characters and ignoring cases.
For example,
“A man, a plan, a canal: Panama” is a palindrome.
“race a car” is not a palindrome.
Note:
Have you consider that the string might be empty? This is a good question to ask during an interview.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/
https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome/
T: O(N), S: O(1)
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
int i = 0, j = s.size()-1;
while(i<=j){
while(i<j && !isalnum(s[i])){++i;}
while(i<j && !isalnum(s[j])){--j;}
if(tolower(s[i++])!=tolower(s[j--])) return false;
}
return true;
}- Python
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, s):
s = [i.lower() for i in s if i.isalnum()]
return s == s[::-1]- Java
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int i=0;
int L=s.length();
int j=L-1;
while(i<j){
while(i<j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(i))) i++;
while(i<j && !Character.isLetterOrDigit(s.charAt(j))) j--;
if(Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(i)) == Character.toLowerCase(s.charAt(j))){
i++;
j--;
}else return false;
}
return true;
}
}29.3 680. Valid Palindrome II
Given a non-empty string s, you may delete at most one character. Judge whether you can make it a palindrome.
Example 1:
Input: “aba”
Output: True
Example 2:
Input: “abca”
Output: True
Explanation: You could delete the character ‘c’.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-palindrome-ii/
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/7618468.html
class Solution {
public:
bool validPalindrome(string s) {
int left = 0, right = s.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (s[left] != s[right])
return isValid(s, left, right - 1) ||
isValid(s, left + 1, right);
++left; --right;
}
return true;
}
bool isValid(string s, int left, int right) {
while (left < right) {
if (s[left] != s[right]) return false;
++left; --right;
}
return true;
}
};- Java
class Solution {
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
int L=s.length();
int l=0;
int r=L-1;
while(l<r){
if(s.charAt(l) != s.charAt(r))
return valid(s,l,r-1)||valid(s,l+1,r);
l++;
r--;
}
return true;
}
boolean valid(String s, int i, int j){
while(i<j) if(s.charAt(i++)!=s.charAt(j--)) return false;
return true;
}
}29.4 Number of All Palindrome Substrings
Given a string, your task is to count how many palindromic substrings in this string.
The substrings with different start indexes or end indexes are counted as different substrings even they consist of same characters.
Example 1:
Input: “abc”
Output: 3
Explanation: Three palindromic strings: “a”, “b”, “c”.
Example 2:
Input: “aaa”
Output: 6
Explanation: Six palindromic strings: “a”, “a”, “a”, “aa”, “aa”, “aaa”.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindromic-substrings
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindromic-substrings
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/count-palindrome-sub-strings-string/
29.4.1 Algo 1: Expansion from current point
Naive的解法是找出所有的substring palindrome,一边找一边计数.T复杂度是: \(O(N^2)\).
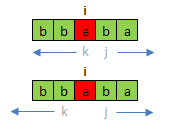
In GFG, it requires length of palindrome substring is greater then or equal to 2.
int countPalindromicSubstring(const char *str){ //O(N^2)
int i,j,k,count=0;
for(i=0;str[i];i++){
k=i-1, j=i+1; //count odd length palindromes
while(k>=0 && str[j] && str[k]==str[j]) ++count, k--, j++;
k=i, j=i+1; //count even length palindrome
while(k>=0 && str[j] && str[k]==str[j]) ++count, k--, j++;
}
return count;.
}这个空间复杂度为O(1).不过麻烦的是需要处理奇数和偶数的情况,所以我觉得速度应该没有下面的DP方法快.面试的时候能写出上面的解法就可以了.
In Leetcode, a single char could be a palindrome. So we need to add string size at the last line.
29.4.2 Algo 2: DP
 需要一個isPalindrome的boolean上三角矩陣,如果是true就加1.
需要一個isPalindrome的boolean上三角矩陣,如果是true就加1.
struct Solution {
int countSubstrings(string s) {
int r = 0, L = s.size();
vector<vector<bool>> isp(L, vector<bool>(L));
// bottom-up loop a upper triangluar matrix
for (int i=L-1;i>=0;i--) // 自底向上,从左到右,平行扫描
for (int j=i;j<L;j++)
if (isp[i][j] = (i==j || s[i]==s[j] && (i+1==j || isp[i+1][j-1]))){
++r;
}
return r;
}
};s[i] == s[j] and (i+1 == j || isp[i+1][j-1]) should be enough.
- JAVA

class Solution {
public int countSubstrings(String s) {
int L=s.length();
boolean[][] P = new boolean[L][L];
int r=0;
for(int i=L-1;i>=0;i--){//这里必须从下往上遍历!!
//for(int i=0;i<L;i++){// Wrong!!!
for(int j=i;j<L;j++){
if(i==j) P[i][j]=true;
else if(i+1==j) P[i][j]=(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j));
else P[i][j]=(P[i+1][j-1]&&(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j)));
//P[i][j] = s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j) && (j<i+3 || P[i+1][j-1]);
if(P[i][j]) r++;
}
}
return r;
}
}- Follow up: 如果要求任意substring包含多少palindrome, 用下面的方法. 用两个矩阵pals和counts. 一个矩阵
pals表示是不是palindrome substring. 另一个矩阵counts表示包含的palindrome substring的个数.
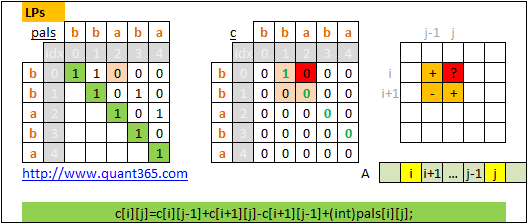
pals[i][j]表示substringA.substr(i,j-i+1)是否是palindrome.
counts[i][j]表示substringA.substr(i,j-i+1)包含多少个palindrome sub-substring.
主要recurrence equation是:
counts[i][j]=counts[i][j-1]+counts[i+1][j]-counts[i+1][j-1]+(int)pals[i][j];
方法和DP解LPs类似. T复杂度也是\(O(N^2)\). 下面是C++代码:
int countPs(const string& s){
int L=s.size();
vector<vector<int>> counts(L,vector<int>(L,0)); // number of palindrome substring
vector<vector<bool>> pals(L,vector<bool>(L,false)); // isPalindrome matrix
for(int i=0;i<L;++i)
pals[i][i]=true;
for(int i=0;i<L-1;++i)
if(s[i]==s[i+1])
pals[i][i+1]=true, counts[i][i+1]=1;// init two matrices
// loop through a matrix diagonally
for(int k=2;k<L;k++){ // K is length
for(int i=0;i<L-k;i++){
int j=k+i;
pals[i][j] = (s[i]==s[j]) && pals[i+1][j-1];
counts[i][j]=counts[i][j-1]+counts[i+1][j]-counts[i+1][j-1]+(int)pals[i][j];
}
}
return counts[0][L-1];
}注意leetcode上面的把单个字符也算成Palindrome.所以结果是: counts[0][L-1]+s.size();
29.4.3 Algo 3: Linear Solution
\(O(N)\)的解法要用到Manacher或者Suffix Array.面试的时候不推荐.
https://www.quora.com/How-can-we-find-the-number-of-palindromic-substrings-in-a-string-in-linear-time
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/20915141/finding-number-of-palindromic-substrings-in-on-or-on-log-n
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_palindromic_substring
29.5 All Palindrome Substrings
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-number-distinct-palindromic-sub-strings-given-string/
这个可以用expansion的方法一个个找出来.
29.6 Longest Palindrome Substring (2D DP, Expansion, Manacher)
 https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
http://fisherlei.blogspot.com/2012/12/leetcode-longest-palindromic-substring.html
http://blog.csdn.net/feliciafay/article/details/16984031
29.6.1 Idea 1: Find a point and expand in two directions

string longestPalindrome(string s) { // Naive Soluton: O(N^2)
int L = s.size();
if (L<=1) return s;
int g = 0, start = 0, k, local, l, r;
for (int i=0; i<L; ++i){ //
k = 1, local = 1;
while((l=i-k)>=0 && (r=i+k)<L){
if (s[l]==s[r]){ local += 2; }else{break;}
++k;
}
if (local>g) g = local, start = i-k+1;
}
for (int i=1; i<L; ++i){
k =0, local=0;
while((l=i-1-k)>=0 && (r=i+k)<L){
if (s[l]==s[r]){ local+=2; }else{break;}
++k;
}
if (local>g) g = local, start = i-k;
}
return s.substr(start, g);
}29.6.2 Idea 2: 2D DP
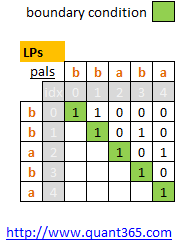
- Recurrence Equation
To tell if arbitrary substring \(A[i:j]\) is a palindrome.
\[
f(i,j)= \begin{cases}
true, & \text{if } (f(i+1,j-1)=true) \text{ and } (A[i]=A[j]) \text{ and } (j > i+1 )\\
true, & \text{if } (A[i]=A[j]) \text{ and } (j = i+1 )\\
false, & \text{otherwise }
\end{cases}
\] where \(i,j\) are index, \(j-i+1\) is the length of pal.
- Boundary Condition
\[f(i,i) = 1\] where \(0\leq i \leq L-1\)
Here we just only used half of the matrix.

Interestingly the boundary condition is the diagonal cells of the matrix from \(M[0][0]\) to \(M[L-1][L-1]\).
- Coding
- how to loop in a half matrix
- fill the half matrix correctly
string longestPalindrome(string s) { // T - O(N^2); S - O(N^2)
int L = s.size(), x = 0, y = 0;
bool U[L][L]; memset(U, 0, L*L*sizeof(bool));// gcc extension
for (int i = 0; i<L; ++i) U[i][i] = true;
for (int j = 0; j<L; ++j)
for (int i = j - 1; i >= 0; --i)
if ((U[i][j] = (j == i + 1) ? (s[i] == s[j]) : (s[i] == s[j] && \
U[i + 1][j - 1])) && (y - x < j - i))
x = i, y = j;
return s.substr(x, y - x + 1);
}29.6.2.1 Idea 3: Manacher (…)
http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/3675788.html
29.6.2.2 Idea 4: Suffix Tree
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/suffix-tree-application-6-longest-palindromic-substring/
29.6.2.3 Idea 5: Rolling Hash
Average \(O(N)\)
http://aleclownes.com/2016/10/03/palindromic-rolling-hash.html
29.7 730. Count Different Palindromic Subsequences
Given a string S, find the number of different non-empty palindromic subsequences in S, and return that number modulo 10^9 + 7.
A subsequence of a string S is obtained by deleting 0 or more characters from S.
A sequence is palindromic if it is equal to the sequence reversed.
Two sequences A_1, A_2, … and B_1, B_2, … are different if there is some i for which A_i != B_i.
Example 1:
Input: S = ‘bccb’
Output: 6
Explanation: The 6 different non-empty palindromic subsequences are ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘bb’, ‘cc’, ‘bcb’, ‘bccb’.
Note that ‘bcb’ is counted only once, even though it occurs twice.
Example 2:
Input: S = ‘abcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcdabcddcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcbadcba’
Output: 104860361
Explanation: There are 3104860382 different non-empty palindromic subsequences, which is 104860361 modulo 10^9 + 7.
https://leetcode.com/problems/count-different-palindromic-subsequences/description/
- CPP
Let dp[len][i][x] be the number of distinct palindromes of the subtring starting at i of length len, where the first (and last) character is x. The DP formula is simple :
If s[i] != x, then dp[len][i][x] = dp[len-1][i+1][x] (ignoring the first character in this window)
If s[i+len-1] != x then dp[len][i][x] = dp[len-1][i][x] (ignoring the last character in this window)
If both the first and last characters are x, then we need to count the number of distinct palindromes in the sub-window from i+1 to i + len -2. Need to be careful with how we count empty string.
Since we only need to subproblems of length len-1, len-2, we only need to remember the solutions for the subproblems of length len, len-1, len-2. This is needed to pass the max test case.class Solution {
public:
int countPalindromicSubsequences(string s) {
int md = 1000000007;
int n = s.size();
int dp[3][n][4];
for (int len = 1; len <=n; ++len) {
for (int i = 0; i + len <=n; ++i){
for (int x = 0; x < 4; ++x){
int &ans = dp[2][i][x];
ans = 0;
int j = i + len - 1;
char c = 'a' + x;
if (len == 1) ans = s[i] == c;
else {
if (s[i] != c) ans = dp[1][i+1][x];
else if (s[j] != c) ans = dp[1][i][x];
else {
ans = 2;
if (len > 2)
for (int y = 0; y < 4;++y) {
ans += dp[0][i+1][y];
ans %=md;
}
}
}
}
}
for (int i=0;i<2;++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
for (int x=0; x < 4;++x)
dp[i][j][x] = dp[i+1][j][x];
}
int ret = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < 4;++x)
ret = (ret + dp[2][0][x]) %md;
return ret;
}
};- Java
class Solution {
int div=1000000007;
public int countPalindromicSubsequences(String S) {
TreeSet[] characters = new TreeSet[26];
int len = S.length();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) characters[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
int c = S.charAt(i) - 'a';
characters[c].add(i);
}
Integer[][] dp = new Integer[len+1][len+1];
return memo(characters,dp, 0, len);
}
public int memo(TreeSet<Integer>[] characters,Integer[][] dp,int start,int end){
if (start >= end) return 0;
if(dp[start][end]!=null) return dp[start][end];
long ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
Integer new_start = characters[i].ceiling(start);
Integer new_end = characters[i].lower(end);
if (new_start == null || new_start >= end) continue;
ans++;
if (new_start != new_end) ans++;
ans+= memo(characters,dp,new_start+1,new_end);
}
dp[start][end] = (int)(ans%div);
return dp[start][end];
}
}29.8 Number of All Palindromic subsequence
Find how many palindromic subsequence (need not necessarily be distinct) can be formed in a given string. Note that the empty string is not considered as a palindrome.
Examples:
Input : str = "abcd"
Output : 4
Explanation :- palindromic subsequence are : "a" ,"b", "c" ,"d"
Input : str = "aab"
Output : 4
Explanation :- palindromic subsequence are :"a", "a", "b", "aa"
Input : str = "aaaa"
Output : 15http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/count-palindromic-subsequence-given-string/
Find how many palindromic subsequence (need not necessarily be distinct) can be formed in a given string. Note that the empty string is not considered as a palindrome.
The above problem can be recursively defined.
Initial Values : i= 0, j= n-1;
CountPS(i,j)
// Every single character of a string is a palindrome
// subsequence
if i == j
return 1 // palindrome of length 1
// If first and last characters are same, then we
// consider it as palindrome subsequence and check
// for the rest subsequence (i+1, j), (i, j-1)
Else if (str[i] == str[j)]
return countPS(i+1, j) + countPS(i, j-1) + 1;
else
// check for rest sub-sequence and remove common
// palindromic subsequences as they are counted
// twice when we do countPS(i+1, j) + countPS(i,j-1)
return countPS(i+1, j) + countPS(i, j-1) - countPS(i+1, j-1) If we draw recursion tree of above recursive solution, we can observe overlapping Subprolems. Since the problem has overlapping subproblems, we can solve it efficiently using Dynamic Programming.
// Function return the total number of all palindromic subsequence
int countPS(string str){
int N = str.length();
vector<vector<int>> cps(N+1,vector<int>(N+1,0));
// check subsequence of length L is palindrome or not
for (int L = 2; L <= N; L++){
for (int i = 0; i<N; i++) {
int j = L + i - 1;
if (j > N) continue;
if (str[i] == str[j])
cps[i][j] = cps[i][j - 1] + cps[i + 1][j] + 1;
else
cps[i][j] = cps[i][j - 1] + cps[i + 1][j] - cps[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
return cps[0][N - 1];
}OJ: https://www.codechef.com/problems/CB03
This is very similar to number of all Palindrome Substring except line 11. 这是有原因的.举例说明’aba’
ab-> s[0], s[1] -> r1=2
ba-> s[1], s[2] -> r2=2
b-> s[1] -> r3=1
s[0]==s[2] -> r4 = 1(s[0],s[2]) + 1*r1 (s[0],s[1],s[2])
total: N = r1+r2+r4-r3 = r1+r2+1 (这里r4-r3永远等于1.)还有这里结果中允许重复字符串.
29.9 All Palindrome Subsequences

另一种表述是一个字符串删除任意字符形成的所有Palindrome: 给一个string, 可以删除任意字符,求所有可以得到的palidrome字串集.
http://www.mitbbs.com/article/JobHunting/33053715_3.html
29.9.1 DFS
网上看到的号称完美解法:无重复的逐一完全遍历所有的substring palindrome.复杂度就是O(the number of palindrome subsequences).
http://www.mitbbs.com/article_t/JobHunting/33053715.html
因为我不懂java和javascript, 所以先记录在这里.
发信人: Ilikemac (一低头的温柔), 信区: JobHunting
标 题: Re: LinkedIn onsite一道题
发信站: BBS 未名空间站 (Mon Nov 9 15:12:19 2015, 美东)
我的java实现,参考了Blaze的思路,不过不知道真正理解了他的思路没有,因为我不
太看得懂javascript.下面是几个点:
1. 这个题目用的是backtracking而不是dp,因为dp不可能给你产生排列组合.dp通常
就是给你一个最值.
2. 时间复杂度是指数级.
3. 题目的本质是产生排列.
4. 一般的backtracking来形成字符串的话,从现有字母集中每次任意挑一个字母,然后
从剩下的字母里继续挑.把所有字母都加到字符串里面去了,这轮程序也就完了.这个
题目因为有个顺序的限制条件,决定程序怎样进行下去并不能用剩下多少字符来决定,
而应该是用已经加入字符串的字母的位置来决定.import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Example5 {
public static void main(String [] args){
Example5 o = new Example5();
List <String> results = o.setUp("abcbabcba");
for(String str: results){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
public List <String> setUp(String palidrome){
HashMap <Character, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap <Character, List<Integer>>();
HashMap <Character, Pointers> locations = new HashMap <Character, Pointers>();
char [] chs = palidrome.toCharArray();
int i = 0;
for(i=0;i<chs.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(chs[i])){ map.get(chs[i]).add(i); }
else{
List <Integer> tmp = new ArrayList <Integer> ();
tmp.add(i);
map.put(chs[i],tmp);
}
}
Set <Character> keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator <Character> iter = keySet.iterator();
List <String > results = new ArrayList <String> ();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Character ch=iter.next();
//results.add(ch.toString());
int size = map.get(ch).size();
locations.put(ch, new Pointers(0,size-1));
}
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder();
dfs(results,0,chs.length-1,sb1,sb2,keySet,map,locations);
return results;
}
private class Pointers {
int left;
int right;
public Pointers(int left, int right){
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public void dfs (List <String> results, int left, int right,
StringBuilder sb1, StringBuilder sb2, Set <Character> keySet,
HashMap < Character, List<Integer>> map, HashMap <Character, Pointers> locations)
{
Iterator <Character> iter = keySet.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
Character ch=iter.next();
//System.out.println("ch="+ch+" left="+left+" right="+right);
Pointers p=locations.get(ch);
//System.out.println("left1="+p.left+" right1="+p.right);
List <Integer> nums = map.get(ch);
int oldLeft = p.left;
int oldRight = p.right;
while((p.left<=p.right)&&(nums.get(p.left)<left)){
p.left++;
}
while((p.left<=p.right)&&(nums.get(p.right)>right)){
p.right--;
}
if(p.left<=p.right){
results.add(sb1.toString()+ch+sb2.toString());
//System.out.println(sb1.toString()+ch+sb2.toString());
}
if(p.left<p.right){
sb1.append(ch);
sb2.insert(0,ch);
int tmp1 = p.left;
int tmp2 = p.right;
p.left++;
p.right--;
//System.out.println(sb1.toString()+sb2.toString());
results.add(sb1.toString()+sb2.toString());
dfs(results,nums.get(tmp1)+1,nums.get(tmp2)-1,sb1,sb2,keySet,map,locations);
sb1.deleteCharAt(sb1.length()-1);
sb2.deleteCharAt(0);
}
p.left = oldLeft;
p.right = oldRight;
}
}
}29.9.2 CLH算法
这里有篇论文专门说这个:Paper
按照论文里面的步骤.代码实现如下:
// Not remove the duplicates
vector<string> allLPS(const string& s) {
int i = 0, j = 0, L=s.size();
vector<pair<int, int>> u1;
for (int i = 0; i < L; ++i)
for (int j = i + 1; j < L; ++j)
if (s[i] == s[j]) u1.emplace_back(i,j);
map<int, vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>> uk;
for (i = 0; i < u1.size(); ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < u1.size(); ++j) {
if (i == j) continue;
if (u1[i].first < u1[j].first && u1[j].second < u1[i].second)
uk[2].push_back({ u1[i],u1[j] });
}
}
for (int k = 3; k <= L / 2; ++k) {
if (uk.count(k - 1) == 0) break;
auto tmp = uk[k - 1];
for (auto e : tmp) {
for (int i = 0; i < u1.size(); i++) {
if (e.back().first<u1[i].first && u1[i].second<e.back().second) {
auto ne = e;
ne.push_back(u1[i]);
uk[k].push_back(ne);
}
}
}
}
vector<string> r;
for (auto pr : u1) {
string tmp(2,s[pr.first]);
r.push_back(tmp);
}
for (auto t : uk) {
for (auto& vpr : t.second){
string tmpstr;
for (auto& pr : vpr) tmpstr += s[pr.first];
string sbar(tmpstr); reverse(sbar.begin(), sbar.end());
string ssbar = tmpstr + sbar;
r.push_back(ssbar);
}
}
return r;
}29.10 516. Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic subsequence’s length in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
Example 1:
Input:
"bbbab"
Output:
4One possible longest palindromic subsequence is “bbbb”.
Example 2:
Input:
"cbbd"
Output:
2One possible longest palindromic subsequence is “bb”.
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindromic-subsequence
Desc: CLRS P405
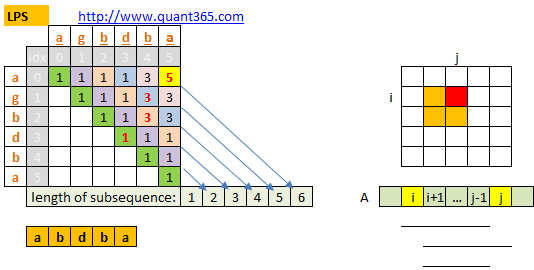
pals[i][j]表示substringA.substr(i,j-i+1)所包含的LPS的长度..
Algorithm:
这个算法先求出LPS的长度.但是不是subsequence本身.要求出本身需要回溯.
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-programming-set-12-longest-palindromic-subsequence/
Top Down:
// Returns the length of the longest palindromic subsequence in seq
int lps(char *seq, int i, int j) {
if (i == j) return 1;
if (seq[i] == seq[j] && i + 1 == j) return 2;
if (seq[i] == seq[j]) return lps (seq, i+1, j-1) + 2;
return max( lps(seq, i, j-1), lps(seq, i+1, j) );
}Bottom Up:
int lps(char *str) {
int n = strlen(str);
int i, j, cl;
int L[n][n]; // Create a table to store results of subproblems
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) L[i][i] = 1;
// cl is length of substring
for (cl=2; cl<=n; cl++) {
for (i=0; i<n-cl+1; i++) {
j = i+cl-1;
if (str[i] == str[j] && cl == 2) L[i][j] = 2;
else if (str[i] == str[j]) L[i][j] = L[i+1][j-1] + 2;
else L[i][j] = max(L[i][j-1], L[i+1][j]);
}
}
return L[0][n-1];
}- JAVA
class Solution {
private int[][] dp;
public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
char[] a=s.toCharArray();
int L=s.length();
dp=new int[L][L];
return LPS(a,0,L-1);
}
private int LPS(char[] a, int h, int t){
if(dp[h][t]>0) return dp[h][t];
if(a[h]==a[t]){
if(h==t) return dp[h][t]=1;
if(h+1==t) return dp[h][t]=2;
return dp[h][t]=2+LPS(a,h+1,t-1);
}
return dp[h][t]=Math.max(LPS(a,h+1,t),LPS(a,h,t-1));
}
}- Super simple solution using reversed string
If you know how to find LCS between 2 strings, then this problems can be reduced to finding the LCS between the original string and its reversed form:
class Solution {
public int longestPalindromeSubseq(String s) {
if (s == null || s.isEmpty()) return 0;
int len = s.length();
int[][] dp = new int[len + 1][len + 1];
String t = new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString();
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = len - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) == t.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i+1][j+1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}Just find length:
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindrome(string s) {
return dp(s,0,s.size()-1);
}
map<int,map<int,int>> m;
int dp(string& s,int h, int t){
if(h>t) return 0;
if(h==t) return 1;
if(h+1==t) return s[h]==s[t]?2:1;
if(m.count(h) and m[h].count(t)) return m[h][t];
if(s[h]==s[t]) return 2+dp(s,h+1,t-1);
return max(dp(s,h,t-1),dp(s,h+1,t));
}
};29.11 Longest Common Subsequence 2
http://www.lintcode.com/en/problem/longest-common-subsequence/
29.12 Longest Increasing Subsequence(LIS) 2
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/
dynamic-programming.html#longest-increasing-subsequencelis
29.13 Palindrome Partitioning (2d DP + subsets DFS)
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
For example, given s = “aab”, Return
[
["aa","b"],
["a","a","b"]
]The DFS part is almost the same as problem subsets.
struct Solution {
VVS partition(string s) {
if (s.empty()){ return VVS();}////????
int L= s.size();
VVB U(L, vector<bool>(L, false));
for(int i=0; i<L; ++i) U[i][i]=true;
for(int j=0; j<L; ++j)
for(int i=j-1;i>=0;--i)
U[i][j] = (i+1==j)? (s[i]==s[j]):(s[i]==s[j] && U[i+1][j-1]);
VVS r;
VS ps;// partial solution
dfs(U, r, ps, s, 0);
return r;
}
void dfs(const VVB& U, VVS& r, VS& ps, const string& s, int head){
if (head==s.size()) r.push_back(ps);
for(int tail=head; tail<s.size(); ++tail){
if (U[head][tail]){
ps.push_back(s.substr(head, tail-head+1));
dfs(U, r, ps, s, tail+1);////dfs(U, r, ps, s, head+1); wrong
ps.pop_back();
}
}
}
};After some optimization:
struct Solution {
VVS partition(string s) {
int L= s.size();
VVB U(L, vector<bool>(L, false));
for(int i=L-1; i>=0; i--)
for(int j=i; j<L; j++)
U[i][j] = (i+1>=j-1 || U[i+1][j-1]) && s[i]==s[j];
VVS r; // full solution
VS p; // partial solution
dfs(U, r, p, s, 0);
return r;
}
void dfs(const VVB& U, VVS& r, VS& ps, const string& s, int head){
if (head==s.size())////
r.push_back(ps);// return can be saved here
for(int tail=head; tail<s.size(); ++tail){
if (U[head][tail]){
ps.push_back(s.substr(head, tail-head+1));
dfs(U, r, ps, s, tail+1);////dfs(U, r, ps, s, head+1); wrong
ps.pop_back();
}
}
}
};29.14 132. Palindrome Partitioning II(2d DP+ 1d DP)
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning-ii/
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return the minimum cuts needed for a palindrome partitioning of s.
For example, given s = “aab”, return 1 since the palindrome partitioning ["aa","b"] could be produced using 1 cut.
cut[i]表示子串s[0…i]所需要的最小分割数

struct Solution {
int minCut(string s) { // 2 dps
int L=s.size();
if(L<=1) return 0;
vector<vector<bool>> U(L,vector<bool>(L));// L by L matrix with all 0
for(int i=L-1;i>=0;--i)// 1. get U
for(int j=i;j<L;++j)
U[i][j]=(j-i<2 || U[i+1][j-1]) && s[i]==s[j];
vector<int> r(L+1,L);
r[0]=-1;
for(int i=1;i<L+1;++i) // 2. get r mincut
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;--j)
if(U[j][i-1]) r[i]=min(r[i],r[j]+1);
return r.back();
}
};29.15 Palindrome Pairs
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-pairs/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-pairs/
Given a list of unique words, find all pairs of distinct indices (i, j) in the given list, so that the concatenation of the two words, i.e. words[i] + words[j] is a palindrome.
Example 1:
Given words = ["bat", "tab", "cat"]
Return [[0, 1], [1, 0]]
The palindromes are ["battab", "tabbat"]Example 2:
Given words = ["abcd", "dcba", "lls", "s", "sssll"]
Return [[0, 1], [1, 0], [3, 2], [2, 4]]
The palindromes are ["dcbaabcd", "abcddcba", "slls", "llssssll"]class pp(object): # T: O(N*K^2) N is len(words), K is E[len(word)]
def palindromePairs(self, words):
wmap = {v : i for i, v in enumerate(words)}
def isPalindrome(word):#O(K)
size = len(word)
for x in range(size / 2):
if word[x] != word[size - x - 1]:
return False
return True
ans = set()
for idx, word in enumerate(words):#O(N)
# 1
if "" in wmap and word != "" and isPalindrome(word):
bidx = wmap[""]
ans.add((bidx, idx))
ans.add((idx, bidx))
# 2
rword = word[::-1]
if rword in wmap:
ridx = wmap[rword]
if idx != ridx:
ans.add((idx, ridx))
ans.add((ridx, idx))
# 3
for x in range(1, len(word)):#O(K^2)
left, right = word[:x], word[x:]
rleft, rright = left[::-1], right[::-1]
if isPalindrome(left) and rright in wmap:
ans.add((wmap[rright], idx))
if isPalindrome(right) and rleft in wmap:
ans.add((idx, wmap[rleft]))
return list(ans)
p = pp()
words = ["", "s", "abcd", "dcba", "lls", "sssll"]
p.palindromePairs(words)29.16 266. Palindrome Permutation
Given a string, determine if a permutation of the string could form a palindrome. For example, “code” -> False, “aab” -> True, “carerac” -> True.
这题结合了Palindrome和Permutation两个重要概念.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-permutation/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-permutation/
因为ASCII码包括扩展的范围是[0,255].所以用类似counting sort的方法.这里不是计数递增,而是不断flip,因为只需判断奇偶性.
29.17 Palindrome Permutation II
Given a string s, return all the palindromic permutations (without duplicates) of it. Return an empty list if no palindromic permutation could be form.
For example:
Given s = “aabb”, return [“abba”, “baab”].
Given s = “abc”, return .
 https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-permutation-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-permutation-ii/
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> generatePalindromes(string s) {
map<char,int> m;
for(char c: s) m[c]++;
int odd=0;
string t;
char c=0;
for(auto e: m){
if(e.second&1) odd++, c=e.first;
t.append(e.second/2, e.first); ////
}
if(odd>1) return {};
auto pm=perm2(t); // permutation II
vector<string> r;
for(string& t: pm){
string o=t;
reverse(t.begin(), t.end());
r.push_back(c==0?(o+t):(o+c+t));
}
return r;
}
vector<string> perm2(string t){
vector<string> r;
string p;
sort(t.begin(), t.end());
vector<bool> vd(t.size());
dfs(r,p,vd,t);
return r;
}
void dfs(vector<string>& r, string& p, vector<bool>& vd, string& t){
if(p.size()==t.size()){r.push_back(p); return;}
for(int i=0;i<t.size();++i){
if(vd[i]) continue;
if(i>0 and t[i]==t[i-1] and !vd[i-1]) continue; // this is why we need to sort t
vd[i]=true;
p+=t[i];
dfs(r,p,vd,t);
vd[i]=false, p.pop_back();
}
}
};29.18 Get Palindrome of a String with replacement
Find the minimum number of operation required to create palindromic string p from S.
https://discuss.codechef.com/questions/86490/linkedin-placement-test-question-get-palindrome-of-a-string-with-replacement
Elina has a string S, consisting of lowercase English alphabetic letters(ie. a-z). She can replace any character in the string with any other character, and she can perform this replacement any number of times. she wants to create a palindromic string p from s such that string p contains the sub string linkedin. it is guaranteed that Elina can create palindromic string p from S. find the minimum number of operation required to create palindromic string p from S. Sample test case are:
First test case: S=“linkedininininin” explanation :
linkedin (i) (n) (i) (n) (i) ni (n)
(n) (i) (d) (e) (k) (l)
p = "linkedinnideknil" output is 6
Second test case: S=“fulrokxeuolnzxltiiniabudyyozvulqbydmaldbxaddmkobhlplkaplgndnksqidkaenxdacqtsskdkdddls”
output is 46
29.19 9. Palindrome Number
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. Do this without extra space.
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x==0) return true;
if(x<0 or x%10==0) return false;
long long r=0, y=x;
while(x) r=10*r+x%10, x/=10;
return r==(long long)y;
}
};If we do care about integer overflow:
29.20 214. Shortest Palindrome
Given a string S, you are allowed to convert it to a palindrome by adding characters in front of it. Find and return the shortest palindrome you can find by performing this transformation.
For example:
Given "aacecaaa", return "aaacecaaa".
Given "abcd", return "dcbabcd".This problem is indeed computing the longest palindromic prefix of a string s.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-palindrome/
https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-palindrome/
Solution 1: Brute Force
struct Solution { // O(N^2) - TLE
bool ispal(const string & s, int h, int t){ // like reverse string
while(h<t) if (s[h++]!=s[t--]) return false;
return h<=t;
}
string shortestPalindrome(string s) {
int r=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i)
ispal(s,0,i) && (r=max(r,i+1));
string t=s.substr(r);
reverse(t.begin(),t.end());
return t+s;
}
};\(O(N)\)的解决方法是基于马拉车和KMP.
Solution 2: Manacher
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/21739/easy-c-manacher
struct Solution { // 6ms
string shortestPalindrome(string s) {
string t = process(s);
int n = t.length(), center = 0, right = 0;
int* palin = new int[n];
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
int i_mirror = 2 * center - i;
palin[i] = (right > i) ? min(palin[i_mirror], right - i) : 0;
while (t[i + palin[i] + 1] == t[i - palin[i] - 1])
palin[i]++;
if (i + palin[i] > right) {
center = i;
right = i + palin[i];
}
}
int pos;
for (int i = n - 2; i; i--) {
if (i - palin[i] == 1) {
pos = palin[i];
break;
}
}
string tail = s.substr(pos);
reverse(tail.begin(), tail.end());
return tail + s;
}
string process(string& s) {
int n = s.length();
string t(2 * n + 3, '#');
t[0] = '$'; t[2 * n + 2] = '%';
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
t[2 * (i + 1)] = s[i];
return t;
}
};Solution 3: KMP
http://bookshadow.com/weblog/2015/05/22/leetcode-shortest-palindrome/
struct Solution { //6ms
string shortestPalindrome(string s) {
string rev_s = s;
reverse(rev_s.begin(), rev_s.end());
string l = s + "#" + rev_s;
vector<int> p(l.size(), 0);
for (int i = 1; i < l.size(); i++) {
int j = p[i - 1];
while (j > 0 && l[i] != l[j])
j = p[j - 1];
p[i] = (j += l[i] == l[j]);
}
return rev_s.substr(0, s.size() - p[l.size() - 1]) + s;
}
};Solution 4: Rolling Hash \(O(MN)\)
How to construct hash? Here we construct two hashes with reverse order.
strinng hash1 hash2
A 1 1
AB 12 21
ABC 123 321
ABCB 1232 2321
ABCBA 12321 12321When we find a palindrome, the two hashes are equal!
自己先写了一次,包含spurious hit检测的.
struct Solution { // 646 ms
string shortestPalindrome(string s){
if (s.size() <= 1) return s;
int r = 0, hash1 = 0, hash2 = 0, BASE=37, POW=1;//
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
hash1 = hash1*BASE+s[i];
hash2 = hash2 + s[i] * POW;
if (i>0 && hash1 == hash2) {
int j = 0, k = i, spurious=0;
while (j < k) if (s[j++] != s[k--]) { spurious = 1; break; }
if(spurious==0) r = i;
}
POW *= BASE;
}
string tmp = s.substr(r+1);//
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
return tmp + s;
}
};注意substr(size_type pos = 0, size_type count = npos)是returns a substring [pos, pos+count),包含pos那一点.
如果不包含spurious hit check, the speed is 3ms! Your runtime beats 94.28% of cpp submissions!!
struct Solution { // 3 ms
string shortestPalindrome(string s){
if (s.size() <= 1) return s;
int r = 0, hash1 = 0, hash2 = 0, BASE=37, POW=1;//
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
hash1 = hash1*BASE+s[i];
hash2 = hash2 + s[i] * POW;
if (hash1 == hash2) r = i;
POW *= BASE;
}
string tmp = s.substr(r+1);//
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
return tmp + s;
}
};See discussion: https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/41599/8-line-o-n-method-using-rabin-karp-rolling-hash
Others:
https://discuss.leetcode.com/topic/47699/accepted-c-solution-easy-to-understand
29.21 Minimum insertions to form a palindrome
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-programming-set-28-minimum-insertions-to-form-a-palindrome/
// Recursive function to find minimum number of insertions
int findMinInsertions(char s[], int h, int t){
// Base Cases
if (h > t) return INT_MAX;
if (h == t) return 0;
if (h+1 == t) return s[h]==s[t];
// Check if the first and last characters are same. On the basis of the
// comparison result, decide which subrpoblem(s) to call
return (s[h] == s[t])? findMinInsertions(s, h+1, t-1):
(min(findMinInsertions(s,h,t-1),findMinInsertions(s,h+1,t)) + 1);
}这道题和edit distance非常相似.
29.22 409. Longest Palindrome
Given a string which consists of lowercase or uppercase letters, find the length of the longest palindromes that can be built with those letters.
This is case sensitive, for example “Aa” is not considered a palindrome here.
Note: Assume the length of given string will not exceed 1,010.
Example:
Input: “abccccdd”
Output: 7
Explanation: One longest palindrome that can be built is “dccaccd”, whose length is 7.
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-palindrome/
class Solution {
public:
int longestPalindrome(string s) {
vector<int> m(256);
for(char c: s) m[c]++;
int r=0;
bool has_odd=false;
for(int i: m){
r+=i/2*2;
if(i&1) has_odd=true;
}
return r+(int)has_odd;
}
};