Chapter 7 String
String is a special char array ended with NULL character \0.
7.1 C++ string functions
isalpha, isalnum, isdigit, tolower, toupper
find(‘\’,start_pos), string::npos, s.erase(0,L), s.substr(1), s.substr(1,2), s.erase(s.begin()), s.append(5,‘x’)
[cling]$ #include <henry.h>
[cling]$ using namespace std;
[cling]$ std::string s("simonwoo");
[cling]$ s.rfind("o")
(unsigned long) 7
[cling]$ s.rfind('o')
(unsigned long) 7
[cling]$ s.rfind('o',0)
(unsigned long) 18446744073709551615
[cling]$ s.rfind('o',0) == string::npos
(bool) true
[cling]$ s.find('o',0)
(unsigned long) 3
[cling]$ s.erase(4,5) // 5 is length
(std::__cxx11::basic_string &) "simo"
[cling]$ s.append(5,'x')
(std::__cxx11::basic_string &) "simoxxxxx"
[cling]$ s.substr(1)
(std::__cxx11::basic_string) "imoxxxxx"
[cling]$ s.substr(1,3)
(std::__cxx11::basic_string) "imo"
[cling]$ s.erase(1)
(std::__cxx11::basic_string &) "s"
[cling]$ s+="imonwoo"
(std::__cxx11::basic_string &) "simonwoo"
[cling]$ s.erase(s.begin())
(std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >::iterator) @0x55fb991298a0
[cling]$ s
(std::string &) "imonwoo"
[cling]$ s.erase(s.begin(),s.end())
(std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >::iterator) @0x55fb9912afc0
[cling]$ s
(std::string &) ""
[cling]$ s="simonwoo"
(std::__cxx11::basic_string &) "simonwoo"
[cling]$ s.find("woo")
(unsigned long) 5
[cling]$ s.find("o",6)
(unsigned long) 6
[cling]$ s.find('o',7)
(unsigned long) 7
[cling]$ s.find("o",8)
(unsigned long) 18446744073709551615
[cling]$ s.erase(remove(s.begin(), s.end(), 'o'),s.end()) // erase all 'o'
(std::__cxx11::basic_string<char, std::char_traits<char>, std::allocator<char> >::iterator) @0x55da465e2630
[cling]$ s
(std::string &) "simnw"7.2 394. Decode String
Given an encoded string, return it’s decoded string.
The encoding rule is: k[encoded_string], where the encoded_string inside the square brackets is being repeated exactly k times. Note that k is guaranteed to be a positive integer.
You may assume that the input string is always valid; No extra white spaces, square brackets are well-formed, etc.
Furthermore, you may assume that the original data does not contain any digits and that digits are only for those repeat numbers, k. For example, there won’t be input like 3a or 2[4].
Examples:
s = "3[a]2[bc]", return "aaabcbc".
s = "3[a2[c]]", return "accaccacc".
s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef", return "abcabccdcdcdef". https://leetcode.com/problems/decode-string/
https://leetcode.com/problems/decode-string/
- Recursion
struct Solution {
string decodeString(string s) {
int i = 0;
return rec(s, i);
}
string rec(string& s, int& i) {
string r;
int m = 0;
for (; i<s.size(); i++) {
if (isalpha(s[i])) r += s[i];
else if (isdigit(s[i])) m = m * 10 + s[i] - '0';
else if (s[i] == '[') {
i++;////
string t = rec(s, i); //
while (m) r += t, m--; // like r.append(m,t); but multiple-append works only for char
} else if (s[i] == ']') return r;////
}
return r;
}
};Google’s Follow up:
- Encode String
Description
折叠的定义如下:
1. 一个字符串可以看成它自身的折叠.记作S ~S
2. X(S)是X(X>1)个S连接在一起的串的折叠.记作X(S) ~SSSS...S(X个S).
3. 如果A ~A', B ~B',则AB ~A'B' 例如,因为3(A) = AAA, 2(B) = BB,所以3(A)C2(B) ~AAACBB,而2(3(A)C)2(B) ~AAACAAACBB给一个字符串,求它的最短折叠.例如AAAAAAAAAABABABCCD的最短折叠为:9(A)3(AB)CCD.
Input
仅一行,即字符串S,长度保证不超过100.Output
仅一行,即最短的折叠长度.Sample Input
NEERCYESYESYESNEERCYESYESYESSample Output
14HINT
一个最短的折叠为:2(NEERC3(YES))题解
dp[l][r]表示l~r的最短折叠长度
即可推出
dp[l][r]=min(r-l+1, dp[l][k]+dp[k+1][r]) where l<=k<rBut an edge case will make this formula fail. If s is a string with 10 repeated abc, then abc9(abc) and 9(abc)abc will be the solution, which is wrong. To fix this, we need to consider当[k+1][r]可以由[l][k]重复得到时还要:
dp[l][r]=min(dp[l][r],dp[l][k]+2+intlen((r-l+1)/(k-l+1)));intlen用来计算一个Natural Number所占位数, 答案就是dp[0][len-1];
struct Solution {
string s;
vector<vector<int>> opt;
bool EdgeCase(int l, int r, int cl, int cr) {
if ((r - l + 1) % (cr - cl + 1) != 0) return 0;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
if (s[i] != s[(i - l) % (cr - cl + 1) + cl]) return 0;
return 1;
}
int intlen(int x) {int t = 0; while (x) { x /= 10; t++; } return t;}
int rec(int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return 1;
if (opt[l][r]) return opt[l][r];
int t = r - l + 1;
for (int i = l; i<r; i++){
t = min(t, rec(l, i) + rec(i + 1, r));
if (EdgeCase(i + 1, r, l, i))
t = min(t, dp(l, i) + 2 + intlen((r - i) / (i - l + 1) + 1));
}
return opt[l][r] = t;
}
int run(const string& s_) {
s = s_;
int L = s.size();
opt = vector<vector<int>>(L, vector<int>(L));
return dp(0, L-1);
}
};T:\(N(O^2)\), ES:\(O(N^2)\)
This is a top-down DP. Very concise!
可以用dp或者opt表示dp数组,矩阵,map等,其实就是一个存储最优值的cache. 用rec()表示dynamic programming函数,因为它一定是recursive function.
7.3 KMP (Knuth Morris Pratt)
KMP算法在面试前应该能手写. 关键是6行的LPPP函数. partial for loop套if else的方法比较好记!
P763 Algorithms 4th Ed.
The KMP matching algorithm uses degenerating property (pattern having same sub-patterns appearing more than once in the pattern) of the pattern and improves the worst case complexity to \(O(n)\).
The key point is to calculate LPPS[]: longest proper prefix which is also proper suffix.
Proper prefix: All the characters in a string, with one or more cut off the end. “S”, “Sn”, “Sna”, and “Snap” are all the proper prefixes of “Snape”.
Proper suffix: All the characters in a string, with one or more cut off the beginning. “agrid”, “grid”, “rid”, “id”, and “d” are all proper suffixes of “Hagrid”.
KMP: http://jakeboxer.com/blog/2009/12/13/the-knuth-morris-pratt-algorithm-in-my-own-words/
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/searching-for-patterns-set-2-kmp-algorithm/
7.4 28. Implement strStr()
 https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr/
https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr/
struct Solution {
vector<int> LPPP(const string& s){ // LPPP function
vector<int> r(s.size());
for (int i=1, j=0; i<s.size();) // j is index, but also number of chars matched
if(s[i]==s[j]) r[i++]=++j; else if(j) j=r[j-1]; else r[i++]=0;
return r;
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
if(needle.empty()) return 0;
vector<int> lppp = LPPP(needle);
for(int i=0, j=0; i<haystack.size();){ // j is number of chars matached
if(haystack[i]==needle[j]){ i++, j++; if(j==needle.size()) return i-j;}
else if(j) j=lppp[j-1]; else i++;
}
return -1;
}
};最难理解的是...else if(j) j=r[j-1];....用--j;应该可行,但是复杂度就不是线性的了.参考CLRS 1006页关于while loop of lines 6-7 的分析.
7.5 459. Repeated Substring Pattern
Given a non-empty string check if it can be constructed by taking a substring of it and appending multiple copies of the substring together. You may assume the given string consists of lowercase English letters only and its length will not exceed 10000.
Example 1: Input: “abab” Output: True
Explanation: It's the substring “ab” twice.
Example 2: Input: “aba” Output: False
 https://leetcode.com/problems/repeated-substring-pattern/
https://leetcode.com/problems/repeated-substring-pattern/
http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/find-given-string-can-represented-substring-iterating-substring-n-times/

struct Solution {
vector<int> LPPP(const string& s){//Longest Proper Prefix Postfix array
vector<int> r(s.size());
for (int i=1, j=0; i<s.size();)// i for s, j for pattern, last LPPP value
if(s[i]==s[j]) r[i++]=++j; else if(j) j=r[j-1]; else r[i++]=0;
return r;
}
bool repeatedSubstringPattern(string str) {
auto lppp = LPPP(str);
return !lppp.empty() && lppp.back()>0 && (str.size()%(str.size()-lppp.back())==0);
}
};One line solution:
return (s+s).substr(1,2*s.size()-1).find(s)!=s.size()-1;
vector<int> r(0); will generate an empty vector.
This problem is also described at CLRS P1012.
7.6 205. Isomorphic Strings
 https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
https://leetcode.com/problems/isomorphic-strings/
Solution: Map + Set
edge case: "ab"->"aa" (false), "ab"->"ca" (true), abc->xab (true)
第二个例子a=>c and b=>a is true can be understand like this. 有个男孩叫a,碰巧有个女孩也叫a,男孩a matches to girl c, and boy b matches to girl a, which is totally fine!
数学上的双射关系. In mathematics, a bijection, bijective function or one-to-one correspondence is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other set, and each element of the other set is paired with exactly one element of the first set. There are no unpaired elements.
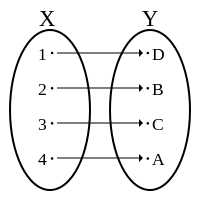
建一个map保存映射关系, 同时用一个set保存被映射的char, 保证同一个char不会被映射两次.
本题难度算是比较简单的.需要注意两种情况:
1. a -> e并且a -> f这种很好用unordered_map<char, char>避免
2. a -> e并且b -> e这种用Hashmap就无能为力了,要再原来的基础上添加一个unordered_set<char>记录string t,检测hashmap和hashset的size()是否相等
struct Solution {
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
if (s.size()!=t.size()) return false;
unordered_map<char,char> m;
bitset<256> bs;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i){
if(m.count(s[i])){
if(m[s[i]]!=t[i]) return false;
} else { // s里面的新东西也是t里面的新东西
if(bs[t[i]]) return false;
m[s[i]]=t[i], bs.set(t[i]);
}
}
return true;
}
};还有种解法,同一个函数调用两次,交换s和t的位置: http://www.voidcn.com/blog/hechunjiao2011/article/p-2798205.html
7.7 290. Word Pattern
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern.
Here follow means a full match, such that there is a bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty word in str.
Examples:
pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return true.
pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish" should return false.
pattern = "aaaa", str = "dog cat cat dog" should return false.
pattern = "abba", str = "dog dog dog dog" should return false.Notes: You may assume pattern contains only lowercase letters, and str contains lowercase letters separated by a single space.
 https://leetcode.com/problems/word-pattern
https://leetcode.com/problems/word-pattern
这个题也是bijection关系,和上题如出一辙.
struct Solution {
bool wordPattern(string pattern, string str) {
unordered_map<char, string> m;
unordered_set<string> ss;
for(char c: pattern){
if(str.empty()) return 0;//
int i=str.find(' ');
if((i!=string::npos) || !str.empty()){
string t = (i!=string::npos) ? str.substr(0,i) : str;
auto it=m.find(c);
if(it != m.end()){
if(it->second != t) return 0; //
}else{
if(ss.count(t)) return 0; //
m[c]=t, ss.insert(t);
}
}
str = (i!=string::npos) ? str.substr(i+1): "";
}
return str.empty();
}
};7.8 291. Word Pattern II
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern.
Here follow means a full match, such that there is a bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty substring in str.
Examples:
pattern = “abab”, str = “redblueredblue” should return true.
pattern = “aaaa”, str = “asdasdasdasd” should return true.
pattern = “aabb”, str = “xyzabcxzyabc” should return false.
Notes: You may assume both pattern and str contains only lowercase letters.
https://leetcode.com/problems/word-pattern-ii
7.8.1 Algo 1: Recursion
基本数据结构和前面的还是一样,一个map,一个set.
struct Solution {
bool wordPatternMatch(string pattern, string str) {
if (pattern.empty()) return str.empty();
if (m.count(pattern[0])) {
const string& t = m[pattern[0]];
if (t.size() > str.size() || str.substr(0, t.size()) != t) return false;
return wordPatternMatch(pattern.substr(1), str.substr(t.size()));
} else {
for (int l = 1; l <= str.size(); ++l) {
string tmp=str.substr(0, l);
if (ss.count(tmp)) continue;
ss.insert(m[pattern[0]] = tmp);
if (wordPatternMatch(pattern.substr(1), str.substr(l))) return true;
m.erase(pattern[0]), ss.erase(tmp); //
}
}
return false;
}
unordered_map<char, string> m;
unordered_set<string> ss;
};7.9 65. Valid Number
 https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-number/
https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-number/
这道题网上的解法说得十分玄乎,实际上是很简单的. 另外Leetcode的test case不完整,没有包含“1E1”这种情况.e可以用大写E.
[cling]$ 1E2
(double) 100.000数字的模式如下图.*表示可以重复0或者多次:
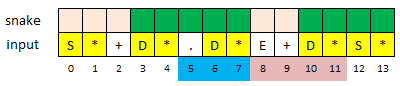
方法就是index不断前进,如果在绿色的位置退出,都是number,如果在浅红色的位置退出就不是number.位置8和9有点类似画蛇添足的感觉.
唯一容易出错的地方是在位置8的时候,之前snake必须为true,不然可以直接返回false.(" +e1")
class Solution(object):
def isNumber(self, s):
i, status, L = 0, 0, len(s)
while(i<L and s[i]==' '): i+=1
if i<L and (s[i]=='+' or s[i]=='-'): i+=1
while i<L and s[i]>='0' and s[i]<='9':
i+=1
status=True
if (i<L and s[i]=='.'):
i+=1
while(i<L and s[i]>='0' and s[i]<='9'):
i+=1
status=True
if i<L and (s[i]=='e' or s[i]=='E'):
if(status==0): return False ####
status=0
i+=1
if i<L and (s[i]=='+' or s[i]=='-'):
i+=1
while i<L and s[i]>='0' and s[i]<='9':
i+=1
status=1
while i<L and s[i]==' ': i+=1
return status==1 and i==LC++:
struct Solution {
bool isNumber(string s) {
bool isnum = false;
int i = 0;
while (s[i] == ' ') i++;
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') i++;
while (isdigit(s[i])) { i++; isnum = true; }
if (s[i] == '.') i++;
while (isdigit(s[i])) { i++; isnum = true; }
if (s[i] == 'e' || s[i] == 'E') {
if (!isnum) return false; //ERROR without it
isnum = false;
i++;
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-') i++;
while (isdigit(s[i])) { i++; isnum = true; }
}
while (s[i] == ' ') i++;
if (i != s.size()) return false;
return isnum;
}
};Regular Expression: [\s]*[-+]?(\\d+\\.?|\\.\\d+)\\d*(e[-+]?\\d+)?[\s]*
值得注意的是NAN,INFINITY其实也是numeric type,根据IEEE 754.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NaN
In computing, NaN, standing for not a number, is a
numeric data type valuerepresenting an undefined or unrepresentable value, especially in floating-point calculations. Systematic use of NaNs was introduced by the IEEE 754 floating-point standard in 1985, along with the representation of other non-finite quantities like infinities.
7.11 635. Design Log Storage System
You are given several logs that each log contains a unique id and timestamp. Timestamp is a string that has the following format: Year:Month:Day:Hour:Minute:Second, for example, 2017:01:01:23:59:59. All domains are zero-padded decimal numbers.
Design a log storage system to implement the following functions:
void Put(int id, string timestamp): Given a log’s unique id and timestamp, store the log in your storage system.
int Retrieve(String start, String end, String granularity): Return the id of logs whose timestamps are within the range from start to end. Start and end all have the same format as timestamp. However, granularity means the time level for consideration. For example, start = “2017:01:01:23:59:59”, end = “2017:01:02:23:59:59”, granularity = “Day”, it means that we need to find the logs within the range from Jan. 1st 2017 to Jan. 2nd 2017.
Example 1:
put(1, "2017:01:01:23:59:59");
put(2, "2017:01:01:22:59:59");
put(3, "2016:01:01:00:00:00");
retrieve("2016:01:01:01:01:01","2017:01:01:23:00:00","Year");
// return [1,2,3], because you need to return all logs within 2016 and 2017.
retrieve("2016:01:01:01:01:01","2017:01:01:23:00:00","Hour");
// return [1,2], because you need to return all logs start from 2016:01:01:01
// to 2017:01:01:23, where log 3 is left outside the range.Note:
There will be at most 300 operations of Put or Retrieve.
Year ranges from [2000,2017]. Hour ranges from [00,23].
Output for Retrieve has no order required.
class LogSystem {
private:
multimap<string, int> log;
string low = "2000:00:00:00:00:00";
string high = "2017:12:31:23:59:59";
unordered_map<string, int> m = {{"Year", 4}, {"Month", 7}, {"Day", 10},
{"Hour", 13}, {"Minute", 16}, {"Second", 19}};
public:
LogSystem() {}
void put(int id, string timestamp) {
log.emplace(timestamp, id);
}
vector<int> retrieve(string s, string e, string gra) {
int len = m[gra];
s = s.substr(0, len) + low.substr(len);
e = e.substr(0, len) + high.substr(len);
auto first = log.lower_bound(s);
auto last = log.upper_bound(e);
vector<int> result;
for (auto it = first; it != last; it++)
result.push_back(it->second);
return result;
}
};注意substr的用法(line 15,16). 还有容易搞混的地方是ID是unique的但是log timestamp并不是,这个也符合工作中的实际情况.所以这里必须用multimap. Again,在RB tree里面range query用lower_bound和upper_bound.
7.12 67. Add Binary
Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string). For example, a = “11”, b = “1”, Return “100”.
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-binary
由于字符串和数字系统的LSB和MSB顺序是相反的,简单的办法是倒过来做.
struct Solution {
string addBinary(string a, string b) {
reverse(a.begin(),a.end()), reverse(b.begin(), b.end());
int x=a.size(), y=b.size(), sum=0, car=0;
string r;
for(int i=0;i<max(x,y);++i){
sum=((i<x)?(a[i]-'0'):0) + ((i<y)?(b[i]-'0'):0) + car;
car=sum/2, sum%=2;
r+=char(sum+'0');
}
if(car) r+=char(car+'0');
reverse(r.begin(), r.end());
return r;
}
};相同算法,不同的写法,代码精简很多,像这样:
7.13 161. One Edit Distance
Given two strings S and T, determine if they are both one edit distance apart.
https://leetcode.com/problems/one-edit-distance/
注意字符顺序是相关的. 比如teacher和detacher就应该返回false. 代码如下:
struct Solution {
bool isOneEditDistance(string s, string t) { // add, del, replace
if(s.size()==t.size()){ // replace?
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i)
if(s[i]!=t[i])
return s.substr(i+1)==t.substr(i+1);
return false;
}else if(abs((int)s.size()-(int)t.size())==1){
if(s.size()<t.size()) swap(s,t); // add?
for(int i=0;i<t.size();++i)
if(s[i]!=t[i])
return s.substr(i+1)==t.substr(i);
}else return 0;
return 1;
}
};第8行有个陷阱,那个int十分重要.参考introduction. Followup就是求edit-distance.
7.14 71. Simplify Path
Given an absolute path for a file (Unix-style), simplify it.
For example,
path = “/home/”, => “/home”
path = “/a/./b/../../c/”, => “/c”
https://leetcode.com/problems/simplify-path/
struct Solution {
string simplifyPath(string path) {
deque<string> q;
size_t t=0;
while((t=path.find('/'))!=string::npos || !path.empty()){
string s;
if(t!=string::npos)
s=path.substr(0,t), path=path.substr(t+1);
else
s=path, path.clear();
if(!s.empty()){
if (s==".."){
if(!q.empty()) q.pop_back();
}else if (s!=".")
q.push_back(s);
}
}
string r;
while(!q.empty())
r+="/"+q.front(), q.pop_front();
return r.empty()?"/":r;
}
};这道题的难度主要是切分字符串. 数据结构除了用deque之外还可以用stack,第5行的|| !path.empty()部分是为了复用while循环内部的逻辑.
7.15 388. Longest Absolute File Path
Suppose we abstract our file system by a string in the following manner:
The string “dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext” represents:
dir
subdir1
subdir2
file.extThe directory dir contains an empty sub-directory subdir1 and a sub-directory subdir2 containing a file file.ext.
The string “dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext” represents:
dir
subdir1
file1.ext
subsubdir1
subdir2
subsubdir2
file2.extThe directory dir contains two sub-directories subdir1 and subdir2. subdir1 contains a file file1.ext and an empty second-level sub-directory subsubdir1. subdir2 contains a second-level sub-directory subsubdir2 containing a file file2.ext.
We are interested in finding the longest (number of characters) absolute path to a file within our file system. For example, in the second example above, the longest absolute path is “dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext”, and its length is 32 (not including the double quotes).
Given a string representing the file system in the above format, return the length of the longest absolute path to file in the abstracted file system. If there is no file in the system, return 0.
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-absolute-file-path/
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/5806493.html
如下图, 问题是从abc.txt到xyz.txt长度该如何调整. 用一个vector
dir
subdir1
file1.ext
subsubdir1
abc.txt
xyz.txt刚开始的时候写下的代码:
struct Solution {
int lengthLongestPath(string input) {
int r=0, i=0, count=0;
vector<int> v;
while ((i=input.find('\n'))!=string::npos || !input.empty()){
if(i==string::npos){
if(v.size()<count+1) v.resize(count+1);
v[count] = ((count>0)?v[count-1]:0) + input.size()+1; // cumulative size
r=max(r, v[count]);
input.clear();
}
if(v.size()<count+1) v.resize(count+1);
v[count] = ((count>0)?v[count-1]:0) + i + 1; // cumulative size
r=max(r, v[count]);
input=input.substr(i+1);
count=0;
while(input[0]=='\t') input=input.substr(1), count++;
}
return r-1;
}
};后来发现题目条件有对文件名和folder名做规定.所以我的提交出现如下错误:
Input:"a\n\tb\n\t\tc"
Output:5
Expected:0加上判断file和folder的条件,代码如下:
struct Solution {
int lengthLongestPath(string input) {
int r=0, i=0, count=0;
vector<int> v;
while ((i=input.find('\n'))!=string::npos || !input.empty()){
if(i==string::npos){
if(input.find('.')==string::npos) return 0;
if(v.size()<count+1) v.resize(count+1);
v[count] = ((count>0)?v[count-1]:0) + input.size()+1; // cumulative size
r=max(r, v[count]);
input.clear();
}
if(v.size()<count+1) v.resize(count+1);
v[count] = ((count>0)?v[count-1]:0) + i + 1; // cumulative size
string s=input.substr(0,i);
if(s.find('.')!=string::npos)
r=max(r, v[count]);
input=input.substr(i+1);
count=0;
while(input[0]=='\t') input=input.substr(1), count++;
}
return r-1;
}
};7.16 482. License Key Formatting
Now you are given a string S, which represents a software license key which we would like to format. The string S is composed of alphanumerical characters and dashes. The dashes split the alphanumerical characters within the string into groups. (i.e. if there are M dashes, the string is split into M+1 groups). The dashes in the given string are possibly misplaced.
We want each group of characters to be of length K (except for possibly the first group, which could be shorter, but still must contain at least one character). To satisfy this requirement, we will reinsert dashes. Additionally, all the lower case letters in the string must be converted to upper case.
So, you are given a non-empty string S, representing a license key to format, and an integer K. And you need to return the license key formatted according to the description above.
Example 1:
Input: S = “2-4A0r7-4k”, K = 4
Output: “24A0-R74K”
Example 2:
Input: S = “2-4A0r7-4k”, K = 3
Output: “24-A0R-74K”
https://leetcode.com/problems/license-key-formatting
这道题让我们对注册码进行格式化,正确的注册码的格式是每四个字符后面跟一个短杠,每一部分的长度为K,第一部分长度可以小于K,另外,字母必须是大写的.那么由于第一部分可以不为K,那么我们可以反过来想,我们从S的尾部往前遍历,把字符加入结果res,每K个后面加一个短杠,那么最后遍历完再把res翻转一下即可,注意翻转之前要把结尾的短杠去掉(如果有的话),参见代码如下:
7.17 616. Add Bold Tag in String
Given a string s and a list of strings dict, you need to add a closed pair of bold tag ‘<b>’ and ‘</b>’ to wrap the substrings in s that exist in dict. If two such substrings overlap, you need to wrap them together by only one pair of closed bold tag. Also, if two substrings wrapped by bold tags are consecutive, you need to combine them.
Examples:
Input: s = “abcxyz123”, dict = [“abc”,“123”]; Output: <b>abc</b>xyz<b>123</b>
Input: s = “aaabbcc”, dict = [“aaa”,“aab”,“bc”]; Output: <b>aaabbc</b>c
Input: s = “zzz”, dict = [“zz”]; Output: <b>zzz</b>
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-bold-tag-in-string
struct Solution { // 86%
string addBoldTag(string s, vector<string>& dict) {
vector<pair<int,int>> v;
for(auto& t: dict){
int be=0;
while((be=s.find(t, be))!=string::npos) //
v.emplace_back(be, be+t.size()), be++;
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
if(v.empty()) return s;
int j=0;
for(int i=1; i<v.size(); ++i) // merge interval
if (v[j].second<v[i].first){
v[++j]=v[i];
}else if (v[j].second<v[i].second)
v[j].second=v[i].second;
int i=0;
string a;
for(int k=0;k<=j;++k){
if(i<v[k].first) a+=s.substr(i, v[k].first-i);
a+="<b>"+s.substr(v[k].first, v[k].second-v[k].first)+"</b>";
i=v[k].second;
}
if(i<s.size())
a+=s.substr(i, s.size()-i);
return a;
}
};注意find带pos的用法: http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/string/basic_string/find
7.18 670. Maximum Swap
Given a non-negative integer, you could swap two digits at most once to get the maximum valued number. Return the maximum valued number you could get.
Example 1: Input: 2736, Output: 7236
Explanation: Swap the number 2 and the number 7.
Example 2: Input: 9973, Output: 9973
Explanation: No swap.
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-swap/
class Solution {
public:
int maximumSwap(int num) {
string s=to_string(num);
string t(s);
sort(t.begin(), t.end(), greater<int>());
if(s==t) return num;
int L=s.size(), i=0;
for(;i<L;++i)
if(s[i]!=t[i]) break; // t[i]>s[i]
int x=s.find_last_of(t[i]);
swap(s[x], s[i]);
return stoi(s);
}
};Note: Here we should use find_last_of because we always want to keep bigger number as foremost as possible. One example is 1993. The result should be 9913, instead of 9193.
7.19 165. Compare Version Numbers
Compare two version numbers version1 and version2. If version1 > version2 return 1, if version1 < version2 return -1, otherwise return 0.
You may assume that the version strings are non-empty and contain only digits and the . character. The . character does not represent a decimal point and is used to separate number sequences. For instance, 2.5 is not “two and a half” or “half way to version three”, it is the fifth second-level revision of the second first-level revision.
Here is an example of version numbers ordering:
0.1 < 1.1 < 1.2 < 13.37
class Solution {
vector<string> split(string& s){
vector<string> r;
int pos=0;
while((pos=s.find('.')) != string::npos){
r.push_back(s.substr(0,pos));
s.erase(0,pos+1); // index, length
}
if(!s.empty()) r.push_back(s);
return r;
}
public:
int compareVersion(string version1, string version2) {
if((version1)==(version2)) return 0;
vector<string> v1=split(version1), v2=split(version2);
int i=0;
for(; i<min(v1.size(), v2.size()); ++i){
if(v1[i]==v2[i]) continue;
if(stoi(v1[i]) > stoi(v2[i])) return 1;
else if(stoi(v1[i]) == stoi(v2[i])) return 0;
return -1;
}
if(v1.size()==v2.size()) return 0;
if(v1.size()>v2.size()){
for(;i<v1.size();++i)
if(stoi(v1[i])>0) return 1;
return 0;
}
for(;i<v2.size();++i)
if(stoi(v2[i])>0) return -1;
return 0;
}
};7.20 6. ZigZag Conversion
The string “PAYPALISHIRING” is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I RAnd then read line by line: “PAHNAPLSIIGYIR”
Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
string convert(string text, int nRows);
convert(“PAYPALISHIRING”, 3) should return “PAHNAPLSIIGYIR”
 https://leetcode.com/problems/zigzag-conversion/
https://leetcode.com/problems/zigzag-conversion/
http://fisherlei.blogspot.com/2013/01/leetcode-zigzag-conversion.html
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int k) {
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
int L = c.length;
StringBuffer[] sb = new StringBuffer[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
sb[i] = new StringBuffer();
int i = 0;
while (i < L) {
for (int idx = 0; idx < k && i < L; idx++) // vertically down
sb[idx].append(c[i++]);
for (int idx = k-2; idx >= 1 && i < L; idx--) // obliquely up
sb[idx].append(c[i++]);
}
return sb[0].toString();
for (int idx = 1; idx < k; idx++)
sb[0].append(sb[idx]);
return sb[0].toString();
}
}7.21 777. Swap Adjacent in LR String
In a string composed of ‘L’, ‘R’, and ‘X’ characters, like “RXXLRXRXL”, a move consists of either replacing one occurrence of “XL” with “LX”, or replacing one occurrence of “RX” with “XR”. Given the starting string start and the ending string end, return True if and only if there exists a sequence of moves to transform one string to the other.
Example:
Input: start = "RXXLRXRXL", end = "XRLXXRRLX"
Output: True
Explanation:
We can transform start to end following these steps:
RXXLRXRXL ->
XRXLRXRXL ->
XRLXRXRXL ->
XRLXXRRXL ->
XRLXXRRLXNote:
1 <= len(start) = len(end) <= 10000.
Both start and end will only consist of characters in {'L', 'R', 'X'}.https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-70/problems/swap-adjacent-in-lr-string/
‘L’ can move to left and ‘R’ can move to right.
class Solution {
public boolean canTransform(String start, String end) {
if (start.length() != end.length()) return false;
int i = 0, j = 0;
int L = start.length();
while (i < L && j < L) {
while (i < L && start.charAt(i) == 'X') i++;
while (j < L && end.charAt(j) == 'X') j++;
if (i == L && j == L) break;
if (i == L || j == L) return false;
if (start.charAt(i) != end.charAt(j)) return false;
if (start.charAt(i) == 'R') {
if (j < i) return false;
} else {
if (i < j) return false;
}
i++; j++;
}
return true;
}
}Another solution but atucally it is also two pointers:
class Solution {
public boolean canTransform(String start, String end) {
if(!start.replace("X", "").equals(end.replace("X", "")))return false;
int L = start.length();
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < L;i++){
if(start.charAt(i) != 'X'){
while(p < L && end.charAt(p) == 'X'){
p++;
}
if(start.charAt(i) == 'R'){
if(i > p)return false;
}else{
if(i < p)return false;
}
p++;
}
}
return true;
}
}7.22 415. Add Strings
Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as string, return the sum of num1 and num2.
Note:
The length of both num1 and num2 is < 5100.
Both num1 and num2 contains only digits 0-9.
Both num1 and num2 does not contain any leading zero.
You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to integer directly.
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-strings/
class Solution {
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2) {
int i=num1.size()-1,j=num2.size()-1,carry=0;
string res="";
while(i>=0||j>=0) {
if(i>=0) carry+=num1[i--]-'0';
if(j>=0) carry+=num2[j--]-'0';
res=to_string(carry%10)+res; // or res=char('0'+carry%10)+res;
carry/=10;
}
return carry?"1"+res:res;
}
};// Oscar Interview
// Create a function to add integers that are represented as strings in binary.
// For example:
// "1001" + "11" = "1100"
/* The numbers to be added are >= 0. We want to steer them away from
simply converting both inputs integers, adding them, and converting
back. Easiest way to do this is to note that the solution must be
capable of accepting arbitrarily large input, so we should handle
numbers that are potentially larger than integer_max.*/
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string f(string x, string y){
string r;
reverse(x.begin(), x.end());
reverse(y.begin(), y.end());
int a=x.size(), b=y.size();
int i=0,j=0;
int sum=0, carry=0;
while(i<a || j<b){
sum=(i<a?(x[i]-'0'):0) + (j<b?(y[j]-'0'):0)+carry;
if(sum==2)sum=0, carry=1; else carry=0;
r+=(sum+'0');
if(i<a)i++;
if(j<b)j++;
}
if(carry)r+=(carry+'0');
reverse(r.begin(), r.end());
return r;
}
int main(int argc, char ** argv){
cout << (f("1001","11") == "1100") << endl;
cout << (f("1001","") == "1001") << endl;
cout << (f("","") == "") << endl;
cout << (f("","1000") == "1000") << endl;
cout << (f("11","1001") == "1100") << endl;
cout << (f("101010","11011") == "1000101") << endl;
return 0;
}7.23 43. Multiply Strings
Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as strings, return the product of num1 and num2.
Note:
The length of both num1 and num2 is < 110.
Both num1 and num2 contains only digits 0-9.
Both num1 and num2 does not contain any leading zero.
You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to
integer directly.https://leetcode.com/problems/multiply-strings/
和加法不同的是这题需要预先分配空间.
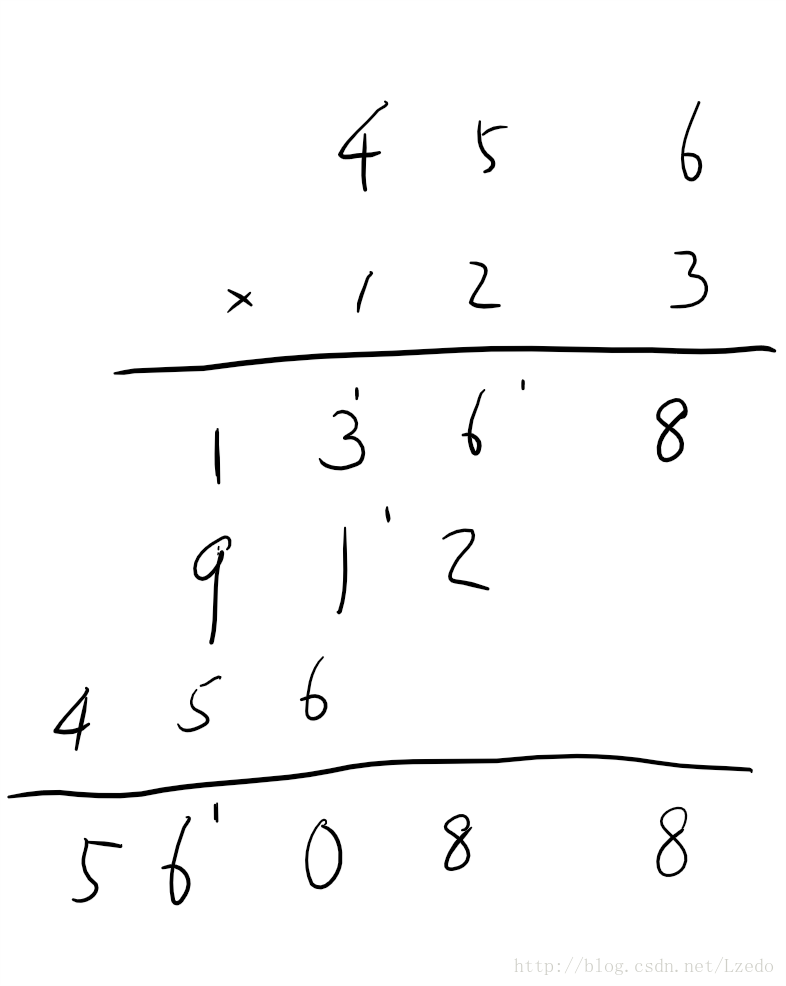
class Solution {
public:
string multiply(string num1, string num2) {
if(num1.empty() || num2.empty()) return "";
reverse(num1.begin(),num1.end());
reverse(num2.begin(),num2.end());
string ret(num1.size()+num2.size(),'0');
for(int j=0; j<num2.size(); j++) {
int carry = 0;
int val = num2[j] - '0';
for(int i=0; i<num1.size(); i++) {
carry += ((num1[i]-'0')*val + (ret[i+j]-'0'));
ret[i+j] = carry%10 + '0';
carry /= 10;
}
if(carry!=0) ret[num1.size()+j] = carry + '0';
}
while(ret.size()!=1 && ret.back()=='0') ret.pop_back(); // 0*999
reverse(ret.begin(),ret.end());
return ret;
}
};题目虽然不难.要完全写对也不容易.
1. 首先要注意num1[i] * num2[j]的结果应该加到ret[i+j]的位置上.
2. 其次要注意ln 16不能遗漏最高位的进位,由于此时ret中该位为0,所以只需要将carry转为字符即可.
3. 最容易遗漏的corner case是ln 18.如999*0 = 0000,此时需要去掉开始的0,但又需要保留最后一个0.
http://bangbingsyb.blogspot.com/2014/11/leetcode-multiply-strings.html
7.24 690. Factorial
Given a number n, return the factorial of the number as a string.
Example: Given a number n = 20, return 2432902008176640000.
#ifndef C690_H
#define C690_H
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string factorial(int n) {
// write your code here
vector<int> res(200000, 0);
int digit = 1,num = 0; //digit表示位数,num表示当前结果
res[0] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i){
int tmp = 0; //当前结果的进位
for (int j = 0; j < digit; ++j)
{
num = res[j] * i + tmp;
res[j] = num % 10;
tmp = num / 10;
}
while (tmp) //tmp不为0,增加位数
{
res[digit] = tmp % 10;
tmp = tmp / 10;
digit++;
}
}
string str;
for (int i = 0; i < digit; ++i)
str = to_string(res[i]) + str;
return str;
}
};
#endifhttps://github.com/jiadaizhao/LintCode/blob/master/0690-Factorial/0690-Factorial.cpp
7.25 271. Encode and Decode Strings
Design an algorithm to encode a list of strings to a string. The encoded string is then sent over the network and is decoded back to the original list of strings.
Machine 1 (sender) has the function:
string encode(vector<string> strs) {
// ... your code
return encoded_string;
}Machine 2 (receiver) has the function:
vector<string> decode(string s) {
//... your code
return strs;
}So Machine 1 does:
string encoded_string = encode(strs);and Machine 2 does:
vector<string> strs2 = decode(encoded_string);strs2 in Machine 2 should be the same as strs in Machine 1.
Implement the encode and decode methods.
Note:
The string may contain any possible characters out of 256 valid ascii characters. Your algorithm should be generalized enough to work on any possible characters. Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your encode and decode algorithms should be stateless. Do not rely on any library method such as eval or serialize methods. You should implement your own encode/decode algorithm.
- CPP
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a list of strings to a single string.
string encode(vector<string>& strs) {
string r;
for(auto s: strs)
r += to_string(s.size())+'/'+s;
return r;
}
// Decodes a single string to a list of strings.
vector<string> decode(string s) {
vector<string> r;
size_t pos=0;
while((pos=s.find('/')) != string::npos){
int len=stoi(s.substr(0,pos));
r.push_back(s.substr(pos+1,len));
s.erase(0,pos+len+1); //
}
return r;
}
};decode函数也可以这样写,不用删除原始字符串:
vector<string> decode(string s) {
vector<string> r;
size_t pos=0, start=0;
while((pos=s.find('/',start)) != string::npos){
int len=stoi(s.substr(start,pos-start));
r.push_back(s.substr(pos+1,len));
start=pos+1+len;
}
return r;
}- JAVA
public class Codec {
// Encodes a list of strings to a single string.
public String encode(List<String> strs) {
if(strs == null || strs.size() == 0) {
return "";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(String s : strs) {
int len = s.length();
sb.append(len);
sb.append('/');
sb.append(s);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// Decodes a single string to a list of strings.
public List<String> decode(String s) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(s == null ||s.length() == 0) {
return res;
}
int index = 0;
while(index < s.length()) {
int forwardSlashIndex = s.indexOf('/', index);
int len = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(index, forwardSlashIndex));
res.add(s.substring(forwardSlashIndex + 1, forwardSlashIndex + 1 + len));
index = forwardSlashIndex + 1 + len;
}
return res;
}
}7.26 293. Flip Game
You are playing the following Flip Game with your friend: Given a string that contains only these two characters: + and -, you and your friend take turns to flip two consecutive “++” into “–”. The game ends when a person can no longer make a move and therefore the other person will be the winner.
Write a function to compute all possible states of the string after one valid move.
For example, given s = “++++”, after one move, it may become one of the following states:
[
"--++",
"+--+",
"++--"
]7.27 294. Flip Game II
You are playing the following Flip Game with your friend: Given a string that contains only these two characters: + and -, you and your friend take turns to flip two consecutive “++” into “–”. The game ends when a person can no longer make a move and therefore the other person will be the winner.
Write a function to determine if the starting player can guarantee a win.
For example, given s = “++++”, return true. The starting player can guarantee a win by flipping the middle “++” to become “+–+”.
Follow up: Derive your algorithm’s runtime complexity.
https://leetcode.com/problems/flip-game-ii/
http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/5226206.html
class Solution {
public:
bool canWin(string s) {
size_t i = -1;
while((i = s.find("++", i + 1)) != s.npos) {
string t=s.substr(0,i)+"--"+s.substr(i+2);
if (!canWin(t)) return true;
}
return false;
}
};7.28 93. Restore IP Addresses
Given a string containing only digits, restore it by returning all possible valid IP address combinations.
For example: “25525511135”, return [“255.255.11.135”, “255.255.111.35”]. (Order does not matter)
https://leetcode.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<String>();
if (s.length()<4||s.length()>12) return res;
dfs(s,"",res,0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(String s, String tmp, ArrayList<String> res, int count){
if (count == 3 && isValid(s)) {
res.add(tmp + s);
return;
}
for(int i=1; i<4 && i<s.length(); i++){
String substr = s.substring(0,i);
if (isValid(substr)){
dfs(s.substring(i), tmp + substr + '.', res, count+1);
}
}
}
public boolean isValid(String s){
if (s.charAt(0)=='0') return s.equals("0");
int num = Integer.parseInt(s);
return num<=255 && num>0;
}
}几点注意的地方:
在验证字符串是否是数字的时候,要注意0的情况,001,010,03都是非法的.所以,如果第一位取出来是0,那么我们就判断字符串是否是“0”,不是的情况都是非法的
取字符串的时候,注意位数不够的问题,不仅<4, 而且<s.length()
注意substring的范围
字符串转换成数字 Integer.parseInt();
别忘了IP 地址里面的 “.”
到第4个Part的时候我们就可以整体验证剩下的所有字符串(因为第4个Part最后一定要取到结尾才是正确的字符串)
7.29 246. Strobogrammatic Number
A strobogrammatic number is a number that looks the same when rotated 180 degrees (looked at upside down).
Write a function to determine if a number is strobogrammatic. The number is represented as a string.
For example, the numbers “69”, “88”, and “818” are all strobogrammatic.
7.30 247. Strobogrammatic Number II
A strobogrammatic number is a number that looks the same when rotated 180 degrees (looked at upside down).
Find all strobogrammatic numbers that are of length = n.
For example, Given n = 2, return [“11”,“69”,“88”,“96”].
https://leetcode.com/problems/strobogrammatic-number-ii
这道题是之前那道Strobogrammatic Number的拓展,那道题让我们判断一个数是否是对称数,而这道题让我们找出长度为n的所有的对称数,我们肯定不能一个数一个数的来判断,那样太不高效了,而且OJ肯定也不会答应.题目中给了提示说可以用递归来做,而且提示了递归调用n-2,而不是n-1.我们先来列举一下n为0,1,2,3,4的情况:
n = 0: none
n = 1: 0, 1, 8
n = 2: 11, 69, 88, 96
n = 3: 101, 609, 808, 906, 111, 619, 818, 916, 181, 689, 888, 986
n = 4: 1001, 6009, 8008, 9006, 1111, 6119, 8118, 9116, 1691, 6699, 8698, 9696,
1881, 6889, 8888, 9886, 1961, 6969, 8968, 9966我们注意观察n=0和n=2,可以发现后者是在前者的基础上,每个数字的左右增加了[1 1], [6 9], [8 8], [9 6],看n=1和n=3更加明显,在0的左右增加[1 1],变成了101, 在0的左右增加[6 9],变成了609, 在0的左右增加[8 8],变成了808, 在0的左右增加[9 6],变成了906, 然后在分别在1和8的左右两边加那四组数,我们实际上是从m=0层开始,一层一层往上加的,需要注意的是当加到了n层的时候,左右两边不能加[0 0],因为0不能出现在两位数及多位数的开头,在中间递归的过程中,需要有在数字左右两边各加上0的那种情况,参见代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findStrobogrammatic(int n) {
return rec(n, n);
}
vector<string> find(int m, int n) {
if (m == 0) return {""};
if (m == 1) return {"0", "1", "8"};
vector<string> t = rec(m - 2, n), res;
for (auto a : t) {
if (m != n) res.push_back("0" + a + "0");
res.push_back("1" + a + "1");
res.push_back("6" + a + "9");
res.push_back("8" + a + "8");
res.push_back("9" + a + "6");
}
return res;
}
};7.31 791. Custom Sort String
S and T are strings composed of lowercase letters. In S, no letter occurs more than once.
S was sorted in some custom order previously. We want to permute the characters of T so that they match the order that S was sorted. More specifically, if x occurs before y in S, then x should occur before y in the returned string.
Return any permutation of T (as a string) that satisfies this property.
Example :
Input:
S = “cba”
T = “abcd”
Output: “cbad”
Explanation:
“a”, “b”, “c” appear in S, so the order of “a”, “b”, “c” should be “c”, “b”, and “a”.
Since “d” does not appear in S, it can be at any position in T. “dcba”, “cdba”, “cbda” are also valid outputs.
https://leetcode.com/problems/custom-sort-string/
My Solution:
class Solution {
public:
string customSortString(string S, string T) {
map<char,int> ss; for(char c: T) ss[c]++;
set<char> sc;
for(char c: S) sc.insert(c), ss[c]--;
string s=S;
for(auto pr: ss){
char c=pr.first;
if(sc.count(c) and ss[c]>0){
int i=s.find(c);
s.insert(i,ss[c],c);
}else if(ss[c]>0){
s.append(ss[c],c);
}
}
return s;
}
};Most concise solution:
class Solution {
public:
string customSortString(string S, string T) {
sort(T.begin(), T.end(),
[&S](char a, char b) { return S.find(a) < S.find(b); });
return T;
}
};- Python